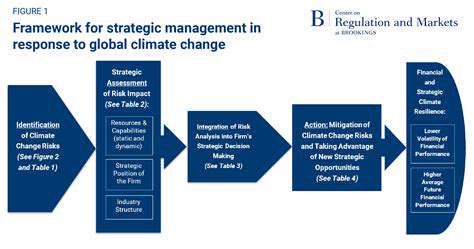
Real Estate Adaptation to Flood Risks
Assessing Flood Risk Zones and Potential Impacts
Understanding Floodplain Delineation
Mapping flood-prone areas through floodplain delineation forms the backbone of comprehensive flood risk assessment. This process doesn't just draw lines on a map - it combines historical flood records, detailed terrain analysis, and water flow patterns to identify vulnerable properties. Urban planners and emergency responders rely on these dynamic maps to implement zoning laws and prepare disaster response plans that could save lives.
The accuracy of these flood risk assessments depends heavily on modern topographic surveys and water flow analysis. Advanced mapping techniques now incorporate real-time rainfall data and climate projections, creating living documents that evolve with our changing environment. These tools help insurance companies set fair premiums and enable homeowners to make informed decisions about flood protection measures.
Evaluating Historical Flood Data
Past flood events tell a compelling story about future risks. By examining flood patterns over decades, researchers can identify neighborhoods that consistently face water intrusion. These historical records often reveal surprising vulnerabilities - areas that flooded a century ago may become inundated again as climate patterns shift.
Analyzing Hydrological Models
Modern flood prediction relies on sophisticated computer simulations that process countless environmental variables. These digital models account for everything from soil absorption rates to anticipated rainfall intensity, creating detailed forecasts of potential flood scenarios. Emergency management teams use these projections to allocate resources strategically before storms hit.
Assessing Elevation and Vulnerability
A property's elevation relative to nearby water sources often determines its flood risk more than absolute height above sea level. Even minor elevation differences of a few feet can mean the difference between staying dry and significant water damage. Modern laser scanning technology (LiDAR) now provides centimeter-accurate elevation data that revolutionizes flood risk assessment.
Exploring Potential Damage and Impacts
The true cost of flooding extends far beyond repair bills. Persistent moisture leads to mold infestations that can render buildings uninhabitable for months, while repeated flooding drives down property values in entire neighborhoods. Many homeowners discover too late that standard insurance policies exclude flood damage, creating financial devastation.
Flood impacts linger long after waters recede. Contaminated floodwaters can poison wells and farmland, while damaged infrastructure may take years to fully restore. The psychological toll on displaced families often goes unmeasured in official damage assessments, yet represents one of flooding's most persistent consequences.
Developing Mitigation Strategies
Forward-thinking communities now implement layered protection systems that combine structural and natural solutions. Elevating buildings represents just one option among many - floodwalls, water-absorbent landscaping, and community drainage projects all play vital roles. The most effective programs combine individual property protections with neighborhood-wide solutions.
Implementing Land-Use Regulations
Zoning laws represent society's first line of defense against flood damage. Progressive municipalities now require climate vulnerability assessments for new developments and mandate elevated construction in floodplains. These regulations not only prevent future losses but help break the cycle of repetitive flood damage claims that burden taxpayers.
Implementing Flood-Resilient Design Strategies
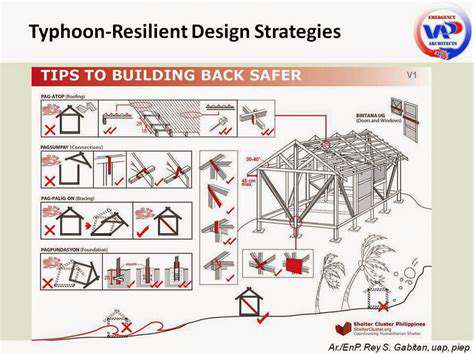
Understanding Flood Hazards
Every flood begins with unique local conditions. Coastal communities face different threats than riverfront towns, requiring tailored solutions. Modern hazard analysis goes beyond static flood maps, incorporating climate change projections and urban development patterns. This dynamic approach helps architects design buildings that will remain safe decades into the future.
Traditional flood maps often fail to account for how new construction alters drainage patterns. Smart communities now require runoff impact studies for all major developments, preventing new buildings from creating flood risks for existing properties.
Designing Flood-Resistant Structures
Innovative construction techniques transform vulnerable buildings into flood-resilient assets. Breakaway walls and sacrificial ground floors allow water to pass through structures with minimal damage, while marine-grade materials withstand prolonged water exposure. The most advanced designs incorporate flood vents that automatically equalize water pressure, preventing structural collapse.
Utilizing Advanced Drainage Systems
Twenty-first century stormwater management treats rainwater as a resource rather than waste. Permeable parking lots and green roofs dramatically reduce runoff while replenishing groundwater supplies. Some cities now integrate underground storage tunnels with smart valves that automatically regulate water flow during storms.
Natural drainage solutions offer multiple benefits beyond flood control. Constructed wetlands filter pollutants while creating wildlife habitats, demonstrating how ecological design can solve engineering challenges. These systems often prove more cost-effective than traditional concrete channels over their lifespan.
Implementing Flood-Proofing Strategies
Comprehensive flood-proofing addresses both obvious and hidden vulnerabilities. Backflow preventers in plumbing systems stop sewage backups, while waterproof electrical systems prevent dangerous shorts. Some buildings now incorporate amphibious foundations that rise with floodwaters, an innovative solution gaining popularity in flood-prone regions.
Critical infrastructure requires special protection measures. Elevating mechanical systems above predicted flood levels ensures hospitals and emergency facilities remain operational during disasters. Many cities now mandate flood-resistant designs for cell towers and power substations that communities rely on during emergencies.
Community Engagement and Education
Effective flood preparedness requires breaking through complacency. Interactive flood simulations and neighborhood drills help residents visualize risks they might otherwise ignore. Some communities establish citizen flood monitoring networks that provide early warnings when waters rise.
Inclusive planning processes yield the most sustainable solutions. When residents help design flood controls, they become invested in maintenance and proper use. This collaborative approach often reveals local knowledge about water flow patterns that engineers might otherwise overlook.

Read more about Real Estate Adaptation to Flood Risks
Hot Recommendations
- Sustainable Real Estate Design Principles
- AI in Real Estate: Streamlining the Buying Process
- Climate Risk Disclosure: A Must for Real Estate
- Climate Risk Analytics: Essential for Real Estate Investment Funds
- Modular Sustainable Construction: Scalability and Speed
- Real Estate and Community Disaster Preparedness
- Smart Buildings and Advanced Building Analytics for Optimal Performance
- Smart Waste Sorting and Recycling in Buildings
- Sustainable Real Estate: A Strategic Advantage
- AI in Real Estate Transaction Processing: Speed and Accuracy