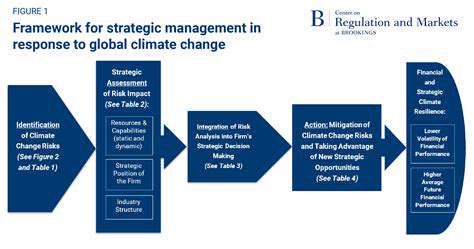
Climate Risk Analysis for Global Real Estate Portfolios
Introduction to Climate-Related Real Estate Risks

Understanding the Scope of Climate-Related Risks
Climate change is no longer a distant threat; its impacts are being felt globally, across diverse sectors, and with increasing urgency. Understanding the full scope of these risks is crucial for effective mitigation and adaptation strategies. This involves recognizing the interconnectedness of climate change with other global challenges, like poverty, inequality, and food security.
The range of potential consequences is vast, spanning from extreme weather events to long-term shifts in ecosystems and resource availability. Climate-related risks are not evenly distributed, disproportionately affecting vulnerable populations and regions. This understanding necessitates a comprehensive approach to risk assessment and management.
The Physical Impacts of Climate Change
Rising global temperatures are driving more frequent and intense heatwaves, droughts, floods, and wildfires. These extreme weather events cause significant damage to infrastructure, disrupt livelihoods, and threaten human health. The increasing frequency and severity of these events underscore the urgent need for adaptation measures.
Sea-level rise, driven by thermal expansion of water and melting glaciers and ice sheets, poses a serious threat to coastal communities and ecosystems. Erosion, saltwater intrusion into freshwater sources, and increased storm surge risk are all critical considerations in planning for the future.
Economic Impacts and Vulnerabilities
Climate change poses substantial economic risks, impacting agriculture, energy, tourism, and other sectors. Damage to infrastructure, disruption of supply chains, and lost productivity can have significant financial consequences. Understanding these economic vulnerabilities is essential for developing effective financial instruments and policies.
The economic costs associated with climate change adaptation and mitigation are substantial, but the costs of inaction are far greater. Investing in sustainable practices and resilient infrastructure is crucial for mitigating long-term economic losses.
Social and Political Implications
Climate change exacerbates existing social inequalities, disproportionately affecting marginalized communities who often lack the resources to adapt. Displacement, migration, and conflict can arise due to resource scarcity and environmental degradation. Addressing these social and political implications requires a just transition to a low-carbon economy.
Political will and international cooperation are essential to effectively address climate-related risks. Global agreements and national policies are crucial in fostering collaboration and encouraging sustainable development practices.
Policy Responses and Solutions
Governments, businesses, and individuals all play critical roles in responding to climate-related risks. Policy responses should focus on mitigation strategies, such as transitioning to renewable energy sources and improving energy efficiency, and adaptation measures, such as building climate-resilient infrastructure and developing early warning systems for extreme weather events. Public awareness campaigns and education are also vital for fostering societal change.
Effective policy implementation requires strong political commitment and adequate funding. International collaboration and knowledge sharing are also crucial to developing and deploying effective solutions.
Future Projections and Uncertainties
Future projections of climate change impacts are complex and uncertain, depending on various factors such as greenhouse gas emissions and regional variations. However, the general consensus is that the impacts will continue to intensify. More research and monitoring are needed to refine these projections and inform effective decision-making.
Understanding the uncertainties in climate projections is crucial for developing flexible and adaptive strategies. The potential for unforeseen consequences necessitates a precautionary approach to climate risk management.
Integrating Climate Change into Portfolio Valuation Models

Integrating Climate Change into Policy
Climate change is no longer a distant threat; its impacts are being felt globally, demanding urgent and comprehensive policy responses. Integrating climate change considerations into existing policies and creating new ones is crucial for mitigating its effects and building resilience. This necessitates a fundamental shift in how governments, businesses, and individuals approach decision-making, moving away from short-term gains to sustainable long-term strategies.
A key aspect of this integration involves understanding the specific vulnerabilities of different sectors and regions. For example, policies addressing water management need to account for changing precipitation patterns, while agricultural policies must adapt to shifting growing seasons and increased extreme weather events. This tailored approach is essential to ensure that policies are effective in addressing the diverse impacts of climate change.
Economic Implications of Climate Action
Transitioning to a low-carbon economy presents both challenges and opportunities for economic development. Investing in renewable energy sources, energy efficiency, and sustainable infrastructure can create new jobs and stimulate innovation, leading to long-term economic growth. However, these investments may require significant upfront costs, potentially impacting industries reliant on fossil fuels. This necessitates careful consideration of economic impacts and the implementation of policies that support a just transition for affected workers and communities.
Policies that incentivize sustainable practices and penalize environmentally harmful activities are crucial. This could include carbon pricing mechanisms, subsidies for renewable energy technologies, and regulations on emissions. These policies will not only mitigate climate change but also promote economic growth in the long run by fostering innovation and efficiency.
Social Equity and Climate Justice
Climate change disproportionately impacts vulnerable populations, exacerbating existing inequalities. Policies aimed at integrating climate change must prioritize social equity and ensure that the benefits of climate action are shared equitably. This includes targeted support for low-income communities and marginalized groups, who often bear the brunt of the effects of climate change, such as extreme weather events and resource scarcity.
Promoting climate education and awareness is a crucial step in empowering individuals and communities to adapt to and mitigate climate change. Access to information and resources, particularly in underserved communities, is vital to facilitate informed decision-making and encourage active participation in climate action initiatives.
International Cooperation and Global Solutions
Climate change is a global challenge that requires international cooperation and coordinated global solutions. International agreements and collaborations are necessary to address the shared responsibility of mitigating climate change. This includes sharing best practices, supporting developing countries in their transition to sustainable development, and fostering technological innovation.
Effective implementation of global policies relies heavily on international collaboration and the commitment of all nations. Stronger international agreements and frameworks are needed to facilitate the exchange of knowledge, resources, and support for a coordinated global response to climate change.
Read more about Climate Risk Analysis for Global Real Estate Portfolios
Hot Recommendations
- Sustainable Real Estate Design Principles
- AI in Real Estate: Streamlining the Buying Process
- Climate Risk Disclosure: A Must for Real Estate
- Climate Risk Analytics: Essential for Real Estate Investment Funds
- Modular Sustainable Construction: Scalability and Speed
- Real Estate and Community Disaster Preparedness
- Smart Buildings and Advanced Building Analytics for Optimal Performance
- Smart Waste Sorting and Recycling in Buildings
- Sustainable Real Estate: A Strategic Advantage
- AI in Real Estate Transaction Processing: Speed and Accuracy