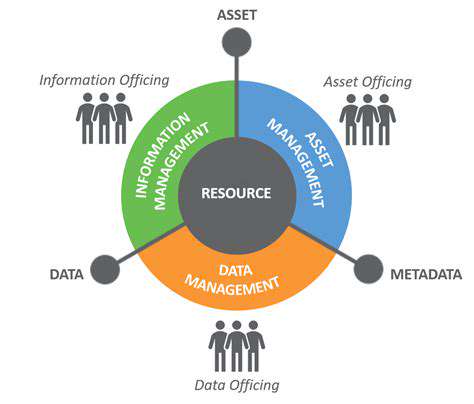
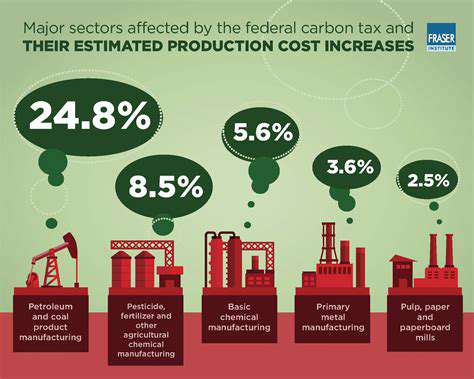
Smart Buildings and Advanced Building Analytics for Optimal Performance
As connected systems continue to evolve, they will undoubtedly reshape various aspects of our lives. The potential applications are virtually limitless, ranging from personalized healthcare to sustainable agriculture. However, the widespread adoption of these technologies also brings forth important considerations regarding data security, privacy, and ethical implications. Addressing these concerns proactively is crucial to ensure that connected systems are used responsibly and beneficially for all.
Furthermore, the increasing reliance on interconnected systems also necessitates robust cybersecurity measures to protect against malicious attacks. Protecting sensitive data and maintaining system integrity are paramount to ensuring the continued success and safety of connected technologies. The integration of these technologies will necessitate a cautious and strategic approach, carefully balancing the potential benefits with the associated risks.
Microorganisms, particularly bacteria and archaea, possess remarkable metabolic capabilities that can be leveraged for enhanced CO2 uptake. Their natural ability to utilize CO2 as a carbon source in various metabolic pathways provides a foundation for engineering strategies. Understanding these pathways, including the Calvin cycle and other CO2 fixation mechanisms, is crucial for designing efficient microbial systems for capturing atmospheric CO2 and converting it into valuable products.
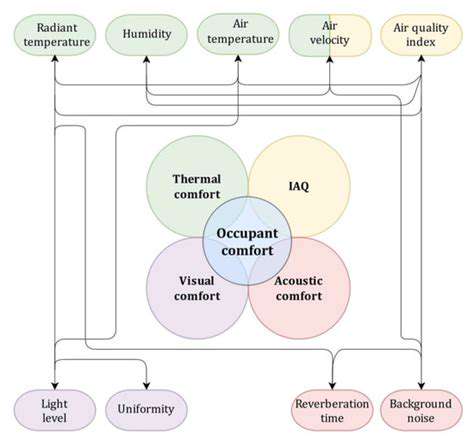
Improving Occupant Comfort and Experience

Optimizing Thermal Comfort
Achieving optimal thermal comfort is crucial for occupant well-being and productivity in any built environment. Factors like temperature, humidity, and air movement significantly influence comfort levels. Understanding the specific needs of occupants, particularly considering their individual preferences and potential sensitivities, is paramount to developing effective strategies. This involves using advanced building systems and smart technologies to dynamically adjust thermal conditions based on real-time occupant feedback and environmental data.
Integrating passive design strategies, such as proper insulation and shading, can significantly reduce the reliance on mechanical systems for thermal control. Employing these strategies can also contribute to energy savings and a more sustainable building operation. Careful consideration must be given to the specific climate conditions and building orientation to ensure optimal thermal performance.
Enhancing Acoustic Conditions
Noise pollution can negatively impact occupant comfort and concentration. Minimizing unwanted noise through strategic material selection and soundproofing techniques is essential for a productive and relaxing environment. Proper sound absorption and reflection considerations are vital to achieving optimal acoustic conditions in the space.
Implementing noise reduction measures, such as installing soundproof windows and doors, can significantly improve the acoustic environment. Effective noise management also involves considering the source of the noise and implementing appropriate solutions to mitigate its impact on occupants.
Promoting Visual Comfort
Adequate natural light and appropriate lighting strategies are critical for occupant visual comfort. Natural light improves mood and well-being, while well-designed artificial lighting systems enhance visibility and reduce eye strain. A balanced approach to lighting, incorporating both natural and artificial sources, is essential for creating a visually appealing and comfortable environment.
Strategies for maximizing natural light, such as careful window placement and design, should be considered. Integrating light-colored finishes and surfaces can also contribute to a brighter and more visually comfortable space. A well-planned lighting scheme, tailored to the specific needs of the occupants, is critical.
Improving Air Quality and Ventilation
Clean and fresh air is essential for occupant health and well-being. Implementing effective ventilation strategies that ensure adequate air exchange and remove pollutants is crucial. Proper ventilation systems should effectively remove stale air and introduce fresh, clean air into the space, enhancing overall air quality.
Integrating technologies that monitor and control indoor air quality, such as sensors for carbon dioxide levels and particulate matter, can ensure that the air remains healthy and comfortable for occupants. Regular maintenance of ventilation systems is crucial for preventing the buildup of pollutants and ensuring optimal performance.
Addressing Ergonomic Considerations
Ergonomic design principles are crucial for creating a comfortable and productive work environment. This involves considering factors like furniture layout, workspace design, and the overall physical space. Implementing adjustable furniture and equipment options to accommodate individual needs is crucial for maximizing comfort and minimizing potential health issues. Ensuring proper posture and movement, minimizing repetitive strain injuries, and maximizing user control over the workspace are paramount.
Creating flexible and adaptable workspaces that allow for various tasks and activities is also important. Providing ample space for movement and minimizing clutter can contribute to a more comfortable and productive environment. This focus on ergonomics ensures that the built environment is not only functional but also supportive of occupant well-being.