Modular Sustainable Construction: Speed and Efficiency
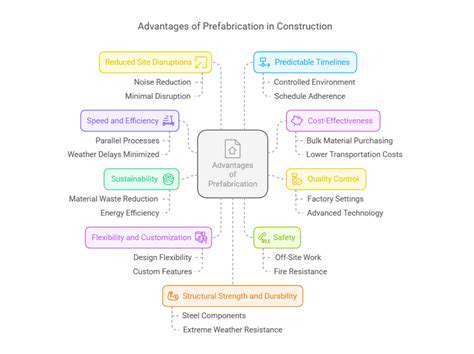
Prefabrication Benefits
Prefabrication, where building components are constructed in a controlled factory setting, delivers significant advantages in terms of speed and efficiency. This method drastically cuts construction timelines by shifting assembly off-site, requiring fewer laborers and minimizing weather-related delays. Workers can then focus on precise installation, enhancing quality control and optimizing resource allocation. The factory environment also reduces clutter and safety hazards commonly found on traditional job sites.
Material waste is another area where prefabrication shines. Factory precision ensures components are cut to exact specifications, virtually eliminating excess materials. This lean approach not only lowers costs but also aligns with sustainable construction practices. Consistent quality checks during manufacturing further reduce defects, ensuring smoother on-site assembly and long-term durability.
Prefabrication in Different Construction Types
While prefabrication is often associated with housing, its applications span far wider. Office complexes, hospitals, and even airports now incorporate prefabricated elements to accelerate project completion. The adaptability of these components allows architects to maintain creative freedom while meeting tight deadlines. Whether replicating historical facades or engineering futuristic designs, prefabrication bridges aesthetics and efficiency.
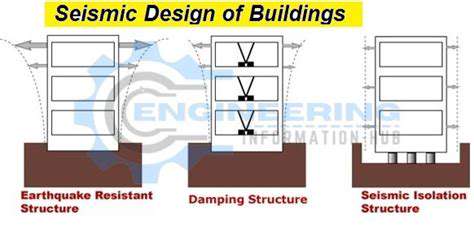
Infrastructure projects particularly benefit from this approach. For example, bridge segments manufactured off-site can be shipped and installed overnight, reducing traffic disruptions and enhancing worker safety. This method also allows for stress-testing components before deployment, ensuring structural integrity in critical applications like tunnels or earthquake-resistant buildings.
Prefabrication and the Future of Construction
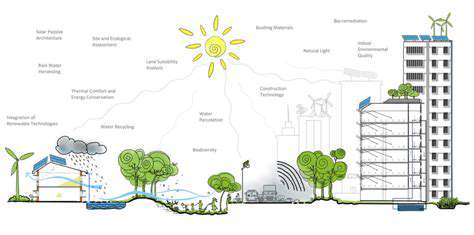
As construction evolves, prefabrication stands at the forefront of industry innovation. Emerging technologies are refining this practice, making it smarter and more sustainable. The reduced carbon footprint from minimized waste and transport efficiency positions prefabrication as an eco-conscious choice for forward-thinking developers.
The marriage of prefabrication with BIM (Building Information Modeling) is revolutionizing project planning. Architects can now simulate entire constructions digitally, identifying potential clashes before fabrication begins. This synergy between virtual and physical construction reduces errors, saves time, and enables more ambitious architectural feats than ever before.

Design Flexibility and Customization in Modular Construction
Design Versatility
Modular construction breaks the mold of rigid design constraints. Architects enjoy unprecedented freedom to experiment with layouts, knowing components can be reconfigured during planning without costly change orders. From sleek contemporary offices to ornate cultural centers, modular techniques preserve design intent while accelerating completion. The factory setting allows for meticulous quality checks on intricate details that might be compromised in traditional builds.
Personalization extends beyond superficial finishes. Homeowners can specify everything from smart home wiring configurations to acoustically optimized wall assemblies during the manufacturing phase. This level of customization was previously only achievable in custom homes with significantly higher budgets and timelines.
Customization Options for Specific Needs
Specialized facilities demonstrate modular construction's adaptive potential. Arctic research stations incorporate insulated wall systems during fabrication, while desert installations integrate passive cooling features. Healthcare modules arrive pre-wired for medical equipment, and educational facilities can include built-in technology infrastructure. This targeted approach ensures buildings perform optimally in their intended environments from day one.
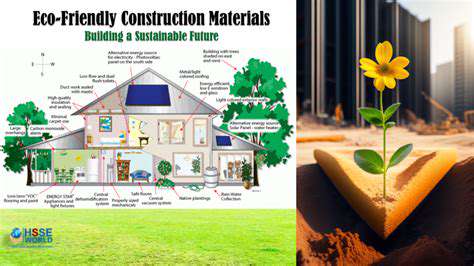
Sustainability is seamlessly woven into modular designs. Factories can install solar-ready roofing, greywater systems, and energy recovery ventilators during production. These integrated solutions often outperform retrofitted systems in both efficiency and reliability.
Tailoring for Specific Client Preferences
The true power of modular construction lies in its ability to reflect individual lifestyles. A photography enthusiast might specify a darkroom module, while a culinary blogger could incorporate a professional-grade kitchen. Unlike cookie-cutter developments, modular projects celebrate unique requirements rather than forcing compromises.
This personalization extends to outdoor spaces. Rooftop gardens, floating decks, and even modular pools can be designed concurrently with the main structure. The result is a cohesive living environment that feels purpose-built rather than mass-produced, proving efficiency and individuality aren't mutually exclusive in construction.
Read more about Modular Sustainable Construction: Speed and Efficiency
Hot Recommendations
- Sustainable Real Estate Design Principles
- AI in Real Estate: Streamlining the Buying Process
- Climate Risk Disclosure: A Must for Real Estate
- Climate Risk Analytics: Essential for Real Estate Investment Funds
- Modular Sustainable Construction: Scalability and Speed
- Real Estate and Community Disaster Preparedness
- Smart Buildings and Advanced Building Analytics for Optimal Performance
- Smart Waste Sorting and Recycling in Buildings
- Sustainable Real Estate: A Strategic Advantage
- AI in Real Estate Transaction Processing: Speed and Accuracy