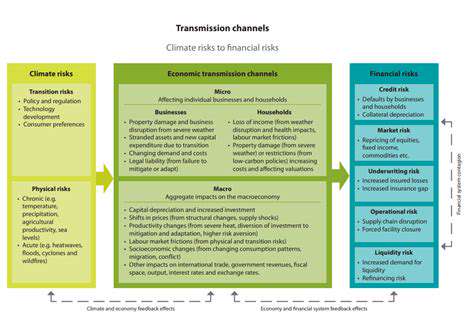
Smart Buildings: The Intersection of Technology and Design
The Power of Data: Enhancing the Occupant Experience
Data-Driven Insights for Personalized Comfort
Smart buildings leverage data to understand occupant behavior and preferences, enabling personalized comfort adjustments. Sensors throughout the building collect real-time information on temperature, humidity, light levels, and even occupancy patterns. This data is then analyzed to identify trends and tailor the environment to individual needs, optimizing comfort and reducing energy consumption. For instance, if a particular office regularly runs cooler than the setpoint, the system can adjust the thermostat in that area to maintain a more comfortable temperature while still adhering to the overall building energy efficiency targets.
By analyzing this collected data, building managers can proactively address potential issues. Early detection of rising temperatures in specific zones, for example, allows for prompt intervention and prevents discomfort for occupants. This proactive approach to environmental control not only enhances the occupant experience but also contributes to operational efficiency.
Optimizing Space Utilization through Data Analysis
Data analytics play a crucial role in understanding how spaces are used within a building. By tracking occupancy patterns across various zones, building managers can identify underutilized areas and optimize space allocation. This can lead to significant cost savings by reducing unnecessary square footage and maximizing the effectiveness of existing resources.
Real-time data on occupancy allows for dynamic adjustments to lighting, temperature, and ventilation systems in different areas. For instance, if a meeting room is empty, the system can automatically lower the temperature and reduce lighting intensity, minimizing energy waste. This intelligent response to real-time occupancy data results in significant energy savings and improved resource management.
Furthermore, this data analysis can inform decisions about future space planning and design. By understanding the preferred workspaces and common usage patterns, architects and building managers can optimize the layout and functionality of the building to better serve the needs of its occupants.
This data-driven approach to space utilization not only improves efficiency but also fosters a more productive and comfortable work environment for building occupants.
Predictive Maintenance and Proactive Building Management
Smart buildings leverage data to predict potential maintenance issues before they arise, allowing for proactive intervention and preventing costly downtime. Sensors monitor various systems, such as HVAC, electrical, and plumbing, providing insights into their performance and identifying potential failures. Early detection of anomalies allows for scheduled maintenance, minimizing disruptions to building operations and ensuring a consistent and comfortable environment for occupants.
Predictive maintenance significantly reduces the risk of unexpected breakdowns, saving time and resources. This proactive approach, facilitated by data analysis, improves reliability and reduces the need for reactive maintenance, ultimately enhancing the building's operational lifespan and reducing maintenance costs.
By analyzing historical data and current performance metrics, the system can predict potential issues, such as equipment malfunctions or system failures. This allows building managers to schedule maintenance before problems escalate, preventing costly repairs and ensuring the continued smooth operation of the building.
Data analysis also allows building managers to anticipate peak energy demands and optimize resource allocation. Understanding energy consumption patterns helps predict future energy needs, enabling proactive adjustments to energy efficiency strategies and reducing overall energy costs.
Innovations in Security and Safety

Enhanced Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication systems are rapidly evolving, moving beyond simple fingerprint scanning to incorporate more sophisticated methods like facial recognition and iris scanning. These advancements significantly improve security by reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Furthermore, the integration of AI-powered algorithms enables these systems to adapt and learn, increasing accuracy and responsiveness over time. This leads to a more secure and user-friendly experience for individuals and organizations alike.
The use of these advanced technologies in various sectors, from banking to healthcare, is transforming how we approach security. They are proving to be a valuable asset in combating fraud and protecting sensitive data. The potential for even more intricate and sophisticated biometric systems in the future is exciting.
Advanced Intrusion Detection Systems
Modern intrusion detection systems (IDS) are no longer simple reactive tools. They employ sophisticated machine learning algorithms to identify and respond to threats in real-time, often anticipating potential attacks before they materialize. This proactive approach minimizes the damage and disruption caused by malicious activity, safeguarding critical infrastructure and data. These systems can also adapt to emerging threats, a crucial element in maintaining robust security in today's rapidly evolving cyber landscape.
Improved Physical Security Measures
Physical security is becoming increasingly integrated with technological advancements. Smart access control systems, utilizing keyless entry and facial recognition technology, are enhancing security in buildings and facilities. These systems provide granular control over who enters and when, creating a more secure environment for personnel and assets.
Advanced surveillance technologies, including high-resolution cameras and sophisticated analytics software, are enhancing the ability to monitor and respond to potential threats in real-time. These measures not only deter criminal activity but also improve overall safety and security.
Cybersecurity Awareness Training
Employee training plays a critical role in strengthening overall security. Comprehensive cybersecurity awareness training programs educate employees about the various threats and vulnerabilities they might encounter. This includes recognizing phishing attempts, protecting sensitive data, and understanding the importance of strong passwords. This proactive approach empowers individuals to make informed decisions and significantly reduces the risk of security breaches.
Secure Data Encryption and Storage
Advanced encryption techniques are being implemented to safeguard data at rest and in transit. These advanced methods increase the difficulty for unauthorized access to sensitive information. The use of end-to-end encryption ensures that data remains protected even if the system or network is compromised. This is a critical step in protecting sensitive data, particularly in sectors like finance and healthcare.
Robust data storage solutions, employing multiple layers of security and redundancy, are crucial. This ensures data availability and integrity, even in the face of unexpected events or attacks. Maintaining data security and integrity is paramount in today's interconnected world.
Predictive Security Analytics
Predictive security analytics leverage historical data and machine learning to identify potential security threats before they cause harm. This advanced technology analyzes patterns and anomalies to flag potential risks, allowing organizations to proactively address vulnerabilities and mitigate potential damage. This approach is becoming increasingly crucial in preventing sophisticated cyber attacks.
Remote Work Security Enhancements
The rise of remote work necessitates new security protocols to safeguard data and systems. Virtual private networks (VPNs) and secure remote access solutions are crucial for protecting sensitive information when accessing company resources from outside the office. Strong authentication methods and robust encryption are essential for secure remote connections.
The focus on secure remote access solutions is paramount in supporting the growing trend of remote work. It is crucial that businesses prioritize these enhancements to maintain a secure and productive environment for remote workers and protect company data. This is a critical area of ongoing development and refinement.

Read more about Smart Buildings: The Intersection of Technology and Design
Hot Recommendations
- Sustainable Real Estate Design Principles
- AI in Real Estate: Streamlining the Buying Process
- Climate Risk Disclosure: A Must for Real Estate
- Climate Risk Analytics: Essential for Real Estate Investment Funds
- Modular Sustainable Construction: Scalability and Speed
- Real Estate and Community Disaster Preparedness
- Smart Buildings and Advanced Building Analytics for Optimal Performance
- Smart Waste Sorting and Recycling in Buildings
- Sustainable Real Estate: A Strategic Advantage
- AI in Real Estate Transaction Processing: Speed and Accuracy