Assessing Physical Risks: Climate Change for Real Estate
Evaluating Heatwave Impacts on Property Values and Occupant Health
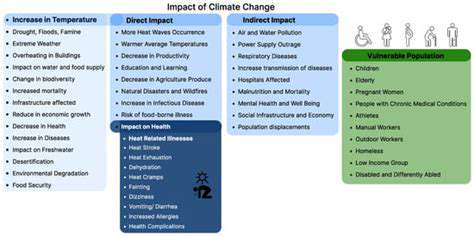
Assessing Physiological Responses
Heatwaves create substantial challenges for professional athletes, affecting both physical performance and health. When core body temperatures rise excessively, muscle strength and endurance decline sharply, directly impairing athletic capabilities. These physiological changes often result in reduced cardiovascular efficiency and diminished cognitive function. Recognizing these patterns helps in crafting targeted heat management approaches.
Athletes face complex bodily reactions under heat stress. Dehydration, frequently occurring during heatwaves, worsens these effects. Maintaining proper hydration with balanced electrolytes proves critical for sustaining peak performance in extreme heat. Keeping internal temperatures stable remains fundamental for both safety and athletic success, yet heat stress disrupts this equilibrium significantly.
Evaluating Performance Metrics
Key indicators like speed, power output, and endurance reveal how heatwaves affect athletes. Tracking these metrics during hot conditions enables immediate detection of performance drops. Notable declines in these measurements often signal dangerous heat stress levels. Studying this data helps pinpoint the exact temperature thresholds where performance starts faltering, allowing for smarter scheduling of training and competitions.
Thorough examination of performance data across varying heat intensities establishes crucial benchmarks. This analysis identifies normal performance ranges in moderate heat and detects when conditions become hazardous. Individual differences matter greatly - factors like personal heat adaptation methods and hydration routines influence how severely heat affects each athlete.
Analyzing Training Adaptations
Gradual heat acclimatization through specialized training represents the most effective defense against heatwave impacts. Proper protocols systematically expose athletes to increasing heat levels, strengthening their body's cooling mechanisms. This method enhances their ability to regulate core temperature even during extreme heat events.
Customized training plans yield the best results for heat tolerance. Considerations must include the specific sport, training loads, and each athlete's unique physiology. Environmental conditions at training locations should also guide program design, ensuring realistic adaptation to expected competition climates.
Impact on Competition Schedules
Heatwaves frequently require modifications to event timing and locations. The duration and intensity of competitions must be carefully weighed against predicted heat conditions. Solutions might involve shifting events to cooler morning hours or selecting venues with better climate control. Such adjustments become essential for protecting athlete welfare.
Venue evaluation must account for heatwave risks. Rule modifications, like mandatory cooling breaks or shortened match durations, may become necessary to ensure safety while maintaining competitive fairness. Critical venue features include adequate shade, cooling stations, and easy access to hydration resources.
Addressing Hydration and Nutrition
Strategic hydration and nutrition form the foundation of heatwave preparedness. Precise fluid and electrolyte management maintains vital bodily functions during heat exposure. Athletes require customized nutrition plans that address both hydration needs and electrolyte replacement, tailored to their sport's specific demands.
Pre-competition hydration strategies make the difference between success and heat illness. Proper fluid intake in the days before events ensures athletes begin competition in optimal hydration states, significantly reducing heat-related health risks.
Long-Term Health Implications
Repeated exposure to extreme heat carries serious health consequences for athletes. Potential cardiovascular strain and cumulative heat illness risks demand attention. Ongoing health monitoring and preventive care prove essential for mitigating these dangers. Athletic organizations must adopt comprehensive health protection programs.
Effective long-term heatwave planning requires integrated approaches. This forward-thinking perspective balances immediate performance needs with lifelong athlete health considerations. Successful implementation depends on collaboration between trainers, medical staff, and sports scientists.
Analyzing Wildfire Risks and Their Implications for Real Estate
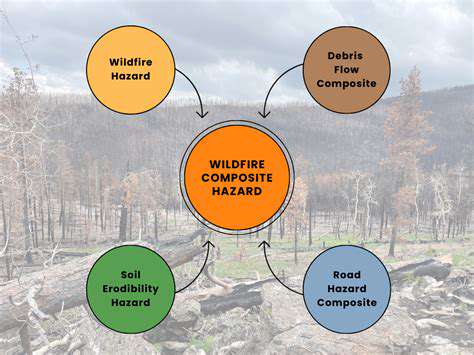
Understanding Wildfire Ignition Sources
Wildfires create devastating property losses, often starting from preventable causes. Human carelessness with fire sources like cigarettes or outdoor cooking accounts for numerous wildfire ignitions. These preventable incidents frequently escalate into major disasters, especially in drought-prone regions.
Natural ignition occurs through lightning strikes, which can spark fires across large areas. Climate shifts have intensified wildfire conditions by extending dry periods and raising temperatures, creating tinderbox environments where fires spread rapidly.
Evaluating Vegetation Density and Type
Vegetation characteristics dramatically influence wildfire behavior. Thick forest canopies enable rapid fire spread through continuous fuel sources. Particularly flammable materials like dry grasses and shrubs ignite easily, allowing fires to move swiftly across landscapes. Local vegetation analysis forms the basis of accurate risk assessment.
Accumulated dead plant matter significantly increases fire danger. Dry leaves, fallen branches, and other debris provide abundant fuel that intensifies wildfires, making regular vegetation management crucial for risk reduction.
Assessing Topography and Wind Patterns
Land formations critically affect fire movement. Sloped terrain channels wind currents, accelerating fire spread. Steep landscapes challenge containment efforts, as traditional firebreaks become less effective. Wind conditions prove equally important, carrying burning embers over long distances to create new fire fronts.
Detailed wind pattern analysis enables better prediction of fire paths, informing strategic placement of fire barriers and emergency resources. Understanding how winds interact with local geography improves prevention planning.
Analyzing Historical Wildfire Data
Historical fire records reveal valuable patterns about regional vulnerabilities. Examining past fire frequency, size, and intensity helps identify high-risk zones requiring special attention. This historical perspective guides effective prevention strategies and prioritizes areas for protective investments.
Developing Risk Management Strategies
Comprehensive wildfire risk plans incorporate multiple protective measures. Effective approaches combine public education about fire safety, proactive land management, and strategic firebreak construction. Well-designed prevention systems dramatically reduce catastrophic wildfire potential. Equally important are clear emergency response protocols and adequate resource allocation.
Implementing Community Preparedness Programs
Local engagement forms the frontline of wildfire defense. Preparedness initiatives should educate residents about fire prevention techniques and emergency procedures. Clear evacuation planning saves lives when wildfires threaten communities. Effective programs empower residents to participate actively in both prevention and response efforts.
Read more about Assessing Physical Risks: Climate Change for Real Estate
Hot Recommendations
- Sustainable Real Estate Design Principles
- AI in Real Estate: Streamlining the Buying Process
- Climate Risk Disclosure: A Must for Real Estate
- Climate Risk Analytics: Essential for Real Estate Investment Funds
- Modular Sustainable Construction: Scalability and Speed
- Real Estate and Community Disaster Preparedness
- Smart Buildings and Advanced Building Analytics for Optimal Performance
- Smart Waste Sorting and Recycling in Buildings
- Sustainable Real Estate: A Strategic Advantage
- AI in Real Estate Transaction Processing: Speed and Accuracy