Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Future
Embracing Eco-Friendly Building Materials and Construction Techniques
Sustainable Materials in Construction
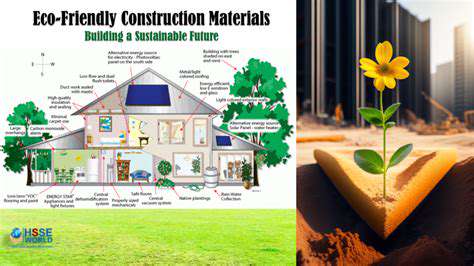
The construction industry is undergoing a transformative shift toward environmentally responsible practices, with material selection playing a pivotal role. Opting for materials derived from renewable sources dramatically decreases dependence on dwindling natural reserves while simultaneously reducing carbon emissions. Innovative options like bamboo flooring, repurposed steel beams, and recycled glass countertops not only match traditional materials in durability but actively contribute to resource conservation.
Beyond their ecological advantages, these sustainable alternatives frequently require significantly less energy during manufacturing processes. This energy efficiency creates a ripple effect, lowering harmful emissions throughout the building's entire existence from construction to eventual decommissioning.
Energy Efficiency in Building Design
Thoughtful architectural planning forms the foundation of energy-conscious construction. Strategic elements such as advanced insulation systems, triple-glazed windows, and intelligent spatial orientation work in harmony to maximize natural advantages. When implemented effectively, these design choices can slash energy usage by up to 40%, producing substantial financial savings while benefiting the environment.
Proper consideration of solar angles, seasonal wind patterns, and thermal mass distribution allows buildings to maintain comfortable temperatures with minimal mechanical intervention. The result is not just reduced utility costs but also spaces that promote occupant health through superior air quality and natural illumination.
Water Conservation Strategies
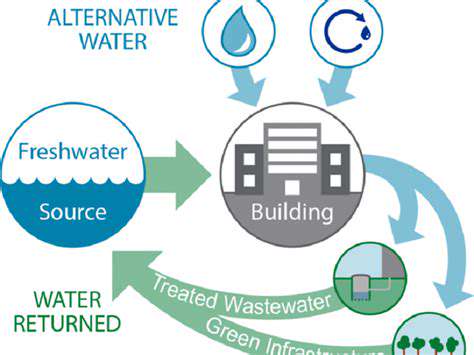
Modern construction practices now incorporate comprehensive water management systems that dramatically reduce consumption. Low-flow plumbing fixtures, graywater recycling mechanisms, and xeriscaping (landscaping that reduces or eliminates the need for irrigation) represent just a few of the innovative approaches. These solutions alleviate pressure on municipal water supplies while providing financial benefits through decreased water bills.
Waste Reduction and Recycling
Progressive construction sites now implement meticulous waste management protocols that go beyond basic recycling. Through precise material estimation, modular construction techniques, and dedicated sorting stations, leading projects achieve up to 90% waste diversion from landfills. This comprehensive approach not only conserves raw materials but also reduces the environmental damage caused by resource extraction and manufacturing.
Specialized handling procedures for hazardous materials ensure safe disposal while preventing soil and groundwater contamination. Many firms now partner with certified recycling facilities to properly process materials like lead-based paints and asbestos-containing products.
Renewable Energy Integration
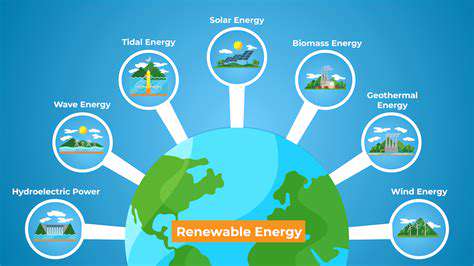
The integration of alternative energy systems represents a quantum leap in sustainable construction. Photovoltaic arrays, small-scale wind turbines, and geothermal heat pumps can transform buildings from energy consumers to energy producers, fundamentally changing their environmental impact. These technologies not only reduce operational costs but also provide energy security in the face of fluctuating utility prices.
Site-specific energy audits help determine the optimal mix of renewable solutions, considering factors like solar exposure, prevailing winds, and subsurface thermal properties. The most advanced projects combine multiple systems to create resilient, self-sufficient energy networks.
Green Building Certifications and Standards
Internationally recognized rating systems like LEED and BREEAM provide structured frameworks for sustainable construction. These comprehensive standards evaluate every aspect of a building's environmental performance, from material sourcing to indoor air quality, creating measurable benchmarks for sustainability. Certification often leads to tangible benefits including tax incentives, higher property valuations, and improved marketability.
Beyond the financial advantages, certified buildings demonstrate a commitment to environmental stewardship that resonates with increasingly eco-conscious consumers and tenants. The rigorous certification process also encourages innovation and continuous improvement in sustainable design practices.

The Economic and Societal Benefits of Sustainable Real Estate
Reduced Environmental Impact
Contemporary real estate development now prioritizes ecological responsibility through innovative approaches that dramatically reduce environmental harm. Advanced construction methodologies combined with low-carbon materials and renewable energy integration create buildings that actively mitigate climate change effects. These structures serve as catalysts for broader environmental improvement by demonstrating practical solutions to resource depletion and pollution.
The circular economy model is gaining traction in the sector, with designers specifying materials that can be easily disassembled and repurposed at the end of a building's life cycle. This paradigm shift reduces extraction of virgin materials while creating new markets for recycled building components.
Improved Energy Efficiency
Modern sustainable properties incorporate cutting-edge technologies that optimize energy performance. Automated building management systems, phase-change materials for thermal regulation, and advanced HVAC solutions work synergistically to minimize energy waste. The resulting reduction in operational costs makes these properties financially attractive while reducing strain on regional power grids.
Enhanced Property Values
The market has demonstrated a clear preference for sustainable properties, with green-certified buildings commanding premium prices. This value appreciation stems from multiple factors including lower operating expenses, future-proof design, and growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible spaces. Investors recognize that sustainability features provide a competitive edge in an increasingly eco-aware marketplace.
Increased Occupant Health and Well-being
Biophilic design principles are transforming modern buildings into spaces that actively enhance human health. Natural ventilation systems, circadian lighting, and non-toxic materials create environments that reduce stress while boosting cognitive function. Employers particularly value these features as they correlate with decreased absenteeism and increased employee productivity in commercial settings.
Economic Growth and Job Creation
The green building sector has emerged as a powerful economic engine, generating employment opportunities across multiple disciplines. From renewable energy technicians to sustainable material researchers, new career paths are developing to support the industry's expansion. This growth stimulates local economies while fostering innovation in related sectors such as manufacturing and technology.
Attracting a Wider Range of Tenants
Environmentally conscious properties demonstrate particular appeal to millennial and Gen Z demographics who prioritize sustainability in their living and working spaces. This demographic shift, combined with corporate sustainability commitments, creates strong demand for green buildings across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. Property owners benefit from reduced vacancy rates and often command premium rental prices.
Community Development and Social Equity
Forward-thinking developers now incorporate community benefits into their sustainability plans. Affordable housing components, public green spaces, and local hiring initiatives ensure that projects deliver value beyond their property lines. This holistic approach to development fosters social cohesion while addressing pressing urban challenges like heat islands and food deserts.
Read more about Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Future
Hot Recommendations
- Sustainable Real Estate Design Principles
- AI in Real Estate: Streamlining the Buying Process
- Climate Risk Disclosure: A Must for Real Estate
- Climate Risk Analytics: Essential for Real Estate Investment Funds
- Modular Sustainable Construction: Scalability and Speed
- Real Estate and Community Disaster Preparedness
- Smart Buildings and Advanced Building Analytics for Optimal Performance
- Smart Waste Sorting and Recycling in Buildings
- Sustainable Real Estate: A Strategic Advantage
- AI in Real Estate Transaction Processing: Speed and Accuracy