The Financial Case for Sustainable Real Estate Investment
Green Buildings and Energy Efficiency: A Financial Edge

Green Building Design Principles
Green building design prioritizes minimizing the environmental impact of structures throughout their lifecycle, from construction to demolition. This holistic approach considers factors like energy efficiency, material sourcing, and waste reduction. By incorporating sustainable practices, green buildings aim to reduce energy consumption, minimize water usage, and lower overall carbon emissions.
Energy Efficiency Measures
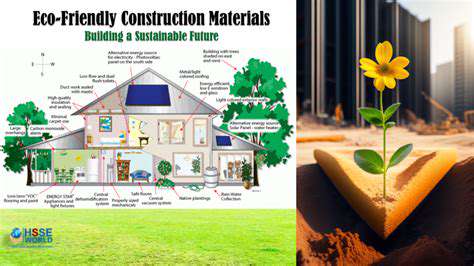
Energy efficiency is a cornerstone of green building design. This involves implementing various strategies to reduce energy consumption in the building. Passive design elements, such as strategically placed windows and shading devices, can significantly reduce the need for active heating and cooling systems. Energy-efficient appliances and lighting systems further contribute to reduced energy usage.
Advanced building automation systems can optimize energy use by adjusting lighting, heating, and cooling based on real-time occupancy and weather conditions. Furthermore, renewable energy sources, like solar panels, can provide a significant portion of the building's energy needs, creating a more sustainable operation.
Sustainable Materials Selection
The choice of building materials plays a crucial role in a building's environmental footprint. Sustainable materials are sourced responsibly, minimizing their impact on the environment. This includes using recycled materials, timber from sustainably managed forests, and locally sourced materials, reducing transportation emissions and supporting local economies. Using materials with low embodied energy is a key component of sustainability.
Waste Reduction and Recycling
Minimizing waste generation throughout the building's lifecycle is a significant aspect of green building practices. This includes implementing strategies for waste reduction during construction, designing for deconstruction and material reuse, and establishing robust recycling programs. Waste reduction and recycling initiatives not only reduce landfill waste but also conserve resources and minimize environmental pollution.
Indoor Environmental Quality
Green buildings prioritize creating a healthy and comfortable indoor environment for occupants. This includes using low-VOC (volatile organic compound) materials, maximizing natural ventilation, and ensuring adequate daylighting. These elements contribute to improved air quality, reducing potential health risks and creating a more productive work or living space. A focus on indoor air quality directly impacts the well-being of occupants.
Economic Benefits of Green Buildings
Green buildings offer substantial economic benefits beyond their environmental advantages. Reduced energy consumption translates to lower utility bills for occupants, leading to cost savings over the building's lifespan. The increased value and marketability of green buildings attract environmentally conscious tenants and buyers, further enhancing their economic viability. Investing in green building practices can result in significant long-term cost savings and increased property value.
Government Policies and Incentives
Government policies and incentives play a vital role in driving the adoption of green building practices. Incentives, such as tax credits and grants, can make green building more financially attractive to developers. Building codes and regulations can also mandate sustainable design elements, encouraging broader adoption and promoting a greener built environment. Government support is essential for fostering a culture of sustainable construction.
Choosing eco-friendly accommodations is a crucial step in reducing the environmental impact of travel. These establishments often incorporate sustainable practices throughout their operations, from energy efficiency and water conservation to waste reduction and the use of locally sourced materials. Looking for certifications like LEED or Green Globe can help you identify accommodations that prioritize environmental responsibility.
Read more about The Financial Case for Sustainable Real Estate Investment
Hot Recommendations
- Sustainable Real Estate Design Principles
- AI in Real Estate: Streamlining the Buying Process
- Climate Risk Disclosure: A Must for Real Estate
- Climate Risk Analytics: Essential for Real Estate Investment Funds
- Modular Sustainable Construction: Scalability and Speed
- Real Estate and Community Disaster Preparedness
- Smart Buildings and Advanced Building Analytics for Optimal Performance
- Smart Waste Sorting and Recycling in Buildings
- Sustainable Real Estate: A Strategic Advantage
- AI in Real Estate Transaction Processing: Speed and Accuracy