Smart Building Occupancy Heat Maps: Space Optimization
Smart building technologies are rapidly transforming the construction and management of buildings worldwide. These technologies leverage advanced sensors, data analytics, and automation to optimize energy consumption, improve occupant comfort, and enhance overall building performance. This shift towards intelligent buildings is driven by the growing need for sustainable practices and the desire to create more efficient and user-friendly spaces.
The integration of these technologies allows for real-time monitoring and control of various building systems, including lighting, HVAC, and security. This dynamic approach enables proactive adjustments to optimize energy use and reduce operational costs. Furthermore, the ability to collect and analyze vast amounts of data provides valuable insights into building performance, facilitating informed decision-making for future improvements.
Enhanced Occupant Experience and Well-being
Smart building technologies go beyond mere efficiency; they significantly enhance the occupant experience. Features like personalized lighting control, automated climate adjustments, and intelligent access systems contribute to a more comfortable and productive environment. These features also promote a sense of security and safety, enhancing overall well-being for those who use the building.
Furthermore, smart buildings can adapt to the specific needs of their occupants. For instance, dynamic lighting and temperature controls can be adjusted based on occupancy patterns and individual preferences, ensuring optimal comfort and reducing energy waste. These personalized adjustments contribute to a more enjoyable and productive workspace or living space.
Sustainable Practices and Environmental Impact
Sustainability is a crucial aspect of modern building design, and smart building technologies play a vital role in achieving this goal. By optimizing energy consumption and reducing waste, these technologies minimize the environmental footprint of buildings. The reduction in energy consumption translates directly to lower carbon emissions and a more sustainable approach to construction and operation.
Smart buildings can also monitor and manage water usage, further enhancing their environmental performance. By integrating water-efficient fixtures and smart irrigation systems, these buildings contribute to responsible water management practices. This holistic approach to sustainability is essential for mitigating the environmental impact of modern development.
Future Trends and Technological Advancements
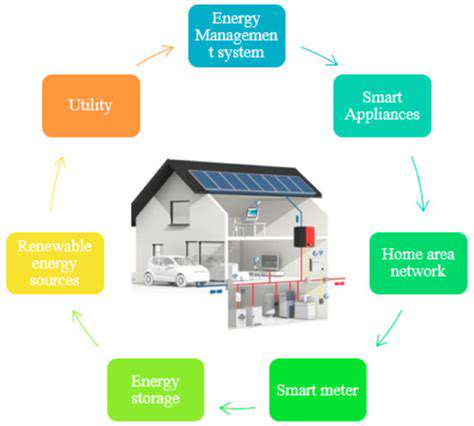
The future of smart building technologies promises even greater advancements. Integration with Internet of Things (IoT) devices, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) is expected to further enhance building automation and optimization. These advanced technologies will enable predictive maintenance, proactive problem-solving, and personalized experiences for occupants.
The integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, within smart building frameworks is also on the rise. This combination will not only enhance energy efficiency but also contribute to a more sustainable and self-sufficient building environment. These advancements will lead to more resilient and environmentally conscious structures for the future.
Space Optimization Strategies: Maximizing Efficiency and Comfort
Maximizing Space Utilization in Modern Smart Buildings
Smart buildings leverage data analytics and automation to optimize space utilization in various ways, from adjusting lighting and temperature based on occupancy to dynamically reconfiguring workspaces. This leads to a more efficient use of existing square footage, reducing wasted space and maximizing the return on investment for building owners.
By tracking occupancy patterns and activity levels, smart building systems can identify underutilized areas and suggest modifications to improve workflow and efficiency. This data-driven approach allows for a more nuanced understanding of how spaces are used, enabling proactive adjustments to improve overall functionality and comfort.
Adaptable Workspaces for Enhanced Productivity
The future of work often involves flexible and adaptable workspaces. Smart buildings facilitate this by offering dynamic and reconfigurable layouts. This flexibility allows spaces to be repurposed quickly to accommodate changing needs, whether for collaborative projects, focused individual work, or impromptu meetings. This adaptability significantly enhances productivity by providing employees with the optimal environment for their tasks.
Smart building technology can automatically adjust the layout based on real-time occupancy data, ensuring that the most suitable configuration is always available. This dynamic approach fosters a more responsive and agile work environment, which in turn boosts employee satisfaction and overall productivity.
Optimizing Energy Consumption
Space optimization strategies often intersect with energy efficiency. Smart buildings use sensors and automation to monitor and manage energy consumption across various systems, including lighting, HVAC, and appliances. This proactive approach to energy management leads to significant cost savings and a reduced carbon footprint.
Automated systems can adjust lighting levels based on natural light availability, regulate temperature based on occupancy, and optimize HVAC performance for maximum efficiency. These strategies minimize energy waste and contribute to a more sustainable building operation.
Smart Lighting Solutions for Enhanced Visual Comfort
Smart lighting systems are crucial for optimizing space and improving the visual comfort of occupants. These systems can adjust lighting levels based on natural light conditions, occupancy, and even the time of day, creating a more dynamic and adaptable environment. The ability to tailor lighting to specific needs fosters a more focused and comfortable work environment.
This proactive approach to lighting control leads to significant energy savings and promotes better visual comfort for employees, contributing to their overall well-being and productivity.
Ergonomic Design and Personalized Comfort
Smart buildings can incorporate data to personalize the comfort of each occupant. Sensors can monitor individual preferences for temperature, lighting, and even air quality, allowing the building to adjust its environment to match those specific needs. This personalized approach to comfort fosters a more positive and productive experience for each employee.
By collecting and analyzing occupant feedback and behavior, smart building systems can learn and adapt to optimize comfort levels over time. This creates a dynamic environment that anticipates and responds to the needs of individual occupants, ultimately improving overall satisfaction and productivity.
Integration with Building Management Systems (BMS)
Smart building optimization strategies rely heavily on effective integration with building management systems (BMS). BMS platforms provide a centralized hub for controlling and monitoring various building systems, allowing for more efficient management of space, energy, and resources. This centralized approach enables a comprehensive view of the entire building's performance, facilitating data-driven decision-making and optimization.
Integration with BMS allows for seamless communication between different building systems, enabling automation and optimization across lighting, HVAC, security, and other functionalities. This comprehensive approach to building management fosters a more sustainable and efficient building operation.
Sustainable Design Principles for Eco-Friendly Spaces
Optimizing space in a smart building often goes hand-in-hand with incorporating sustainable design principles. Features like natural light integration, efficient HVAC systems, and the use of recycled materials contribute to the creation of eco-friendly spaces. This approach not only reduces the environmental impact of the building but also enhances the overall experience for occupants.
Sustainable design practices contribute to a healthier and more productive work environment. By minimizing the building's environmental footprint, smart buildings promote a more responsible and sustainable approach to building design and operation.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Applications and Future Trends
Leveraging Advanced Features
Advanced applications often require more than just basic functionalities. Understanding how to utilize features like custom integrations, sophisticated data manipulation, and complex algorithms is crucial for maximizing application performance and achieving desired outcomes. This deeper understanding empowers developers to craft solutions that go beyond the surface level and address more complex problems.
Exploring these advanced features allows applications to adapt to unique user needs and integrate seamlessly with existing systems. Developers can create applications that are more robust, efficient, and capable of handling a wider range of tasks.
Optimizing Performance for Scalability
As applications grow, performance optimization becomes paramount. Understanding techniques for handling large datasets, minimizing latency, and ensuring responsiveness under heavy loads is essential for a scalable application. Efficient resource management is crucial for maintaining optimal performance as the application's user base expands.
Employing caching strategies, load balancing techniques, and database optimization are vital components in building applications that perform reliably and consistently, even when faced with increased demand.
Security Considerations in Advanced Applications
Advanced applications often handle sensitive data, necessitating robust security measures. Understanding vulnerabilities, implementing secure coding practices, and incorporating data encryption techniques are paramount. Protecting user data and maintaining confidentiality is a key responsibility for developers.
Regular security audits and penetration testing are essential to identify and address potential weaknesses in the application's architecture, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected.
Data Management and Analysis
Effective data management and analysis are integral to advanced applications. Understanding how to collect, process, and interpret data is essential for extracting valuable insights and making informed decisions. This data-driven approach allows applications to adapt and evolve based on user behavior and market trends.
Advanced applications often involve complex data pipelines, requiring expertise in data warehousing, ETL processes, and data visualization techniques. These techniques are crucial for transforming raw data into actionable information.
User Experience (UX) Design for Sophisticated Needs
A seamless user experience is critical for advanced applications. Designing intuitive interfaces, implementing efficient navigation, and providing clear feedback mechanisms are essential for user satisfaction and engagement. A well-designed user experience significantly impacts user adoption and satisfaction.
Integration and Interoperability
Advanced applications frequently need to interact with other systems and services. Understanding integration strategies, API design principles, and data exchange protocols is crucial for seamless interoperability. Effective integration allows for seamless data flow and enhances the application's capabilities.
Choosing the right integration methods and ensuring data compatibility are essential for creating powerful and versatile applications that can work with other systems.
Testing and Deployment Strategies
Robust testing and deployment strategies are critical for the success of advanced applications. Employing comprehensive testing methodologies, including unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing, ensures the application functions as intended. Thorough testing minimizes the risk of unexpected errors and ensures a stable application.
Effective deployment strategies, including cloud-based solutions, containerization, and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, guarantee smooth and reliable deployment processes for advanced applications.
The Impact on Sustainability and Cost Savings

The Growing Need for Sustainable Practices
The increasing global awareness of environmental issues has spurred a significant shift towards sustainable practices across various sectors. Consumers are demanding products and services that minimize their environmental footprint, and businesses are responding by incorporating sustainable strategies into their operations. This growing emphasis on sustainability is driving innovation and creating opportunities for businesses to develop environmentally friendly solutions.
From reducing carbon emissions to conserving resources, the urgency to adopt sustainable practices is becoming more critical every day. This shift is not just about protecting the environment; it's also about ensuring the long-term viability of our resources and creating a more resilient future for generations to come. Sustainable practices are becoming increasingly important for companies to maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Environmental Challenges and Solutions
Climate change, deforestation, and pollution are some of the most pressing environmental challenges facing our planet. These issues have far-reaching consequences, impacting ecosystems, economies, and human well-being. Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach involving government regulations, corporate responsibility, and individual actions.
Transitioning to renewable energy sources, promoting responsible waste management, and conserving water resources are crucial steps in mitigating these environmental issues. Investing in research and development for sustainable technologies is essential to finding innovative solutions and driving progress towards a greener future.
Sustainable agriculture practices, like reducing pesticide use and promoting biodiversity, are also vital for preserving our natural resources and ensuring food security. These practices can contribute to a more resilient agricultural system that can withstand future environmental challenges.
Protecting and restoring ecosystems is paramount for maintaining biodiversity and supporting the health of our planet. Conservation efforts, coupled with sustainable land management practices, can help safeguard these critical environments.
Corporate Responsibility and Consumer Demand
Companies are increasingly recognizing the importance of incorporating sustainability into their core business strategies. This involves minimizing their environmental impact throughout their supply chains and operations, and implementing eco-friendly practices in their production processes. Transparency and accountability in their sustainability efforts are crucial for building trust with consumers.
Consumer demand for sustainable products and services is driving businesses to adopt more environmentally conscious practices. Consumers are actively seeking brands that align with their values and prioritize ethical sourcing and responsible manufacturing. This consumer demand is creating a market for sustainable products and driving innovation in the industry.
Furthermore, many consumers are willing to pay a premium for products that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability. This presents a significant opportunity for businesses to capitalize on the growing market for sustainable goods while also contributing to a more environmentally responsible future.