Climate Risk and Real Estate Due Diligence: A Deep Dive

Identifying Potential Hazards
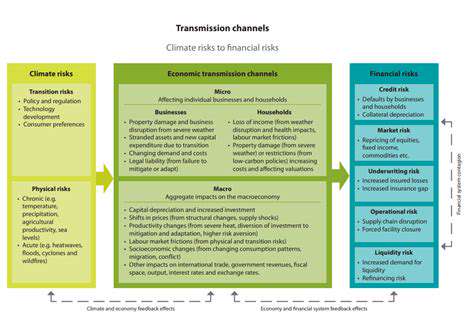
A proactive approach to physical risk assessment begins with identifying potential hazards in any given environment. This requires a methodical review of structural elements, environmental conditions, and operational processes. Spotting these hazards early is the cornerstone of effective prevention and mitigation efforts. Creating a detailed inventory of materials, equipment, and workflows helps in understanding where accidents or injuries might occur.
It's equally important to examine how these elements interact with human activities. Recognizing scenarios that could lead to physical harm—whether from slips, falls, or exposure to dangerous substances—helps in crafting safer environments.
Evaluating Exposure Levels
After pinpointing potential hazards, the next step is to assess how often and how severely people might be exposed to them. Grasping the potential scale of an incident is fundamental to managing risks effectively. Key considerations include how frequently exposure occurs, how long it lasts, and the concentration of any hazardous materials involved.
Analyzing Potential Impacts
A thorough examination of the possible consequences of identified hazards is essential. This means looking at how severe an incident could be, how long its effects might last, and whether it could trigger additional problems. By understanding the full range of possible outcomes, organizations can develop more targeted mitigation strategies. This analysis should cover potential injuries, damage to property, environmental harm, and disruptions to business operations.
Developing Control Measures
Effective risk management hinges on creating robust control measures. These strategies are designed to reduce both the likelihood and severity of incidents, safeguarding people and assets. Putting these controls into action is vital for minimizing potential harm. Options include engineering solutions, administrative protocols, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
Implementing and Monitoring Controls
Successful risk management doesn’t stop at planning—it requires diligent implementation and ongoing oversight. Regular monitoring ensures that controls remain effective and adapt to new challenges. This involves scheduled inspections, audits, and mechanisms for feedback to keep safety measures up to date.
Reviewing and Updating Assessments
Risk assessments should never be static. They need periodic reviews to account for changes in the environment, processes, or technology. Keeping assessments current ensures they remain relevant and effective. This iterative process is key to maintaining a proactive stance on safety and risk management.
Communicating Findings and Recommendations
Clear communication of risk assessment results is critical for effective risk management. This means sharing identified risks, implemented controls, and monitoring procedures with all relevant parties. Transparent communication helps stakeholders understand their roles in maintaining a safe environment. Proper documentation of the assessment process and outcomes is also essential for accountability and future reference.
Integrating Climate Change Scenarios into Valuation Models
Understanding Climate Change Impacts
Incorporating climate change scenarios into real estate valuation models is essential for evaluating long-term property viability and risks. Key impacts like rising sea levels, more frequent extreme weather, and shifting precipitation patterns can significantly influence property values, rental income, and location desirability. Analyzing historical climate data and future projections is crucial for accurate assessments.
Geographic location also plays a pivotal role in climate vulnerability. Coastal properties, for example, face higher risks from sea-level rise and storms, while inland areas may grapple with flooding or drought. Recognizing these localized risks is critical for creating accurate valuation models.
Developing Climate Change Scenarios
Constructing realistic climate change scenarios is a foundational step in valuation. These scenarios should cover a spectrum of potential future conditions, accounting for uncertainties in temperature, precipitation, and extreme weather. This range of possibilities enables a more resilient assessment of property impacts.
Using multiple climate models and projections can provide a broader perspective on risks. Selecting reliable models tailored to specific regions ensures the accuracy and relevance of the scenarios.
Assessing Property Vulnerability
Evaluating how individual properties might be affected by climate change is vital. Factors like building design, materials, proximity to water, and flood risk all contribute to vulnerability. Tools like geographic information systems (GIS) can help map risk zones and predict potential damages.
Impact on Property Values
Climate change can dramatically alter property values. Properties in high-risk areas may see declines, while those in less vulnerable locations could gain value. Accurate impact assessments are crucial for making informed investment decisions. Valuation models that integrate climate scenarios provide a clearer picture of long-term property worth and returns.
Integration into Valuation Models
Incorporating climate scenarios into valuation models demands a structured approach. Models should account for potential shifts in property values, rental income, and operating costs. Including adaptation strategies—like flood defenses or resilient materials—can further refine these models. Specialized software and tools are often necessary to handle the complexities of climate-related risks, ensuring more accurate and comprehensive analyses.
Proactive Strategies for Climate Resilience and Adaptation
Understanding Climate Change Impacts on Real Estate
Climate change is now a present reality, with tangible effects on real estate markets. Rising sea levels, extreme weather, and shifting precipitation patterns are reshaping property values, insurance costs, and location viability. Understanding these impacts is the first step toward building resilience.
Analyzing historical data, future projections, and regional vulnerabilities helps identify specific risks. Thorough due diligence can prevent costly mistakes and ensure long-term investment stability.
Evaluating Property Vulnerability and Risk Assessment
A detailed risk assessment should uncover a property’s specific climate vulnerabilities. This includes evaluating construction materials, location risks, and potential disruptions. Historical weather data, climate projections, and local regulations all play a role in precise assessments. Resilience evaluations—such as structural integrity and emergency preparedness—are equally important.
Developing Climate-Resilient Design and Construction Practices
Adopting climate-resilient design and construction practices can enhance property value and longevity. Sustainable materials, green infrastructure, and water-efficient designs reduce vulnerability and improve environmental performance. These measures often lower operational costs and appeal to eco-conscious buyers.
Implementing Adaptation Strategies for Real Estate Investors
Investors must develop adaptive strategies to navigate climate challenges. Diversifying portfolios to include less vulnerable locations and incorporating climate risks into valuation models are key steps. Proactive adjustments ensure investments remain viable in a changing climate.
Promoting Sustainable Practices and Policy Advocacy
Beyond individual efforts, broader policy advocacy and sustainable practices are essential for climate resilience. Supporting stricter building codes, green infrastructure, and renewable energy initiatives fosters collective action. Community engagement and education also play a vital role in building a resilient future.
Read more about Climate Risk and Real Estate Due Diligence: A Deep Dive
Hot Recommendations
- Sustainable Real Estate Design Principles
- AI in Real Estate: Streamlining the Buying Process
- Climate Risk Disclosure: A Must for Real Estate
- Climate Risk Analytics: Essential for Real Estate Investment Funds
- Modular Sustainable Construction: Scalability and Speed
- Real Estate and Community Disaster Preparedness
- Smart Buildings and Advanced Building Analytics for Optimal Performance
- Smart Waste Sorting and Recycling in Buildings
- Sustainable Real Estate: A Strategic Advantage
- AI in Real Estate Transaction Processing: Speed and Accuracy