Smart Building IoT Platforms: Seamless Integration
The Core Concept of Smart Building IoT Platforms
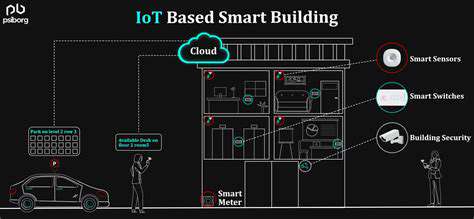
Defining Smart Buildings
Smart buildings leverage advanced technologies to optimize building performance and enhance the user experience. This encompasses a wide range of systems, from automated lighting and HVAC controls to integrated security and access management, all working together to create a more efficient, comfortable, and secure environment. This integration is crucial to achieving the full potential of a smart building.
A key element of smart building design is the seamless integration of various systems. This interconnectedness allows for real-time data analysis and proactive responses to changing conditions. For example, occupancy sensors can adjust lighting and temperature settings automatically, minimizing energy consumption and maximizing occupant comfort.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
One of the most significant benefits of smart building technology is its contribution to energy efficiency and sustainability. By monitoring energy consumption in real-time and identifying areas for improvement, smart buildings can significantly reduce their environmental footprint. This leads to lower operating costs and a smaller carbon footprint, contributing to a more sustainable future.
Smart building management systems can optimize energy usage across the entire building. These systems can learn from patterns and adjust settings accordingly, ensuring that energy is used only when and where it's needed. This proactive approach to energy management is a crucial aspect of sustainable building practices.
Improved Occupant Comfort and Experience
Smart buildings are designed to enhance the overall occupant experience. By tailoring environmental controls to individual preferences and occupancy patterns, smart buildings create a more personalized and comfortable environment. This enhanced comfort translates into increased productivity and satisfaction for building occupants.
Smart lighting systems and personalized temperature controls are just two examples of how smart buildings improve occupant comfort. These features contribute to a more pleasant and productive work or living environment, improving the quality of life for building occupants.
Enhanced Security and Safety
Security is a paramount concern in any building, and smart building technology plays a vital role in enhancing security measures. Integrated access control systems, video surveillance, and automated alarm systems create a more secure environment for occupants and visitors. This proactive approach to security significantly reduces the risk of incidents and protects valuable assets.
Data Analytics and Building Optimization
The interconnected nature of smart buildings allows for comprehensive data collection and analysis. This data provides valuable insights into building performance, occupancy patterns, and energy usage. This data-driven approach allows for continuous improvement and optimization of building operations.
Data analytics from smart building systems empower building managers to identify trends and make data-driven decisions. By analyzing this data, managers can optimize maintenance schedules, improve energy efficiency, and enhance the overall building experience. This is a crucial element in creating a truly intelligent and responsive building.
Key Components for Seamless Integration
Data Acquisition and Processing
A crucial aspect of seamless integration in smart building IoT platforms is the ability to reliably acquire and process data from various sources. This encompasses everything from sensor readings, such as temperature, humidity, and occupancy levels, to data from building management systems (BMS) and other connected devices. Robust data acquisition protocols and efficient data processing pipelines are essential to ensure real-time insights and actionable intelligence. This includes techniques for filtering noise, normalizing data, and handling potential data discrepancies, all of which are critical for accurate analysis and effective decision-making.
The platform needs to support diverse data formats and ensure data integrity throughout the entire process. Proper data validation and storage mechanisms are vital to prevent errors and maintain the reliability of the collected information.
Device Connectivity and Communication
Seamless integration relies heavily on the ability of the platform to connect and communicate with various devices and systems within the building. This includes establishing secure and reliable connections with sensors, actuators, and other smart devices. The platform must support various communication protocols, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and MQTT, to accommodate diverse hardware and network configurations. Interoperability between different devices and systems is essential for a smooth workflow.
Efficient communication protocols are essential to ensure real-time data exchange and enable quick responses to changes in the building environment. The platform should also incorporate mechanisms for handling potential communication failures and ensuring data reliability.
Building Management System (BMS) Integration
Effective integration with existing building management systems (BMS) is critical for a smooth transition to a smart building environment. The platform needs to seamlessly interface with the BMS to leverage existing infrastructure and data. This integration should allow for the exchange of critical information, such as energy consumption data, HVAC settings, and security access controls. It's also vital to ensure a smooth flow of information between the BMS and the IoT platform, allowing for automated responses and control adjustments.
User Interface and Experience
A well-designed user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) are essential for the effective operation of a smart building IoT platform. This includes intuitive dashboards, real-time monitoring tools, and easy-to-understand reporting mechanisms for both building managers and occupants. A user-friendly interface significantly improves the overall user experience and ensures that the platform is readily usable by a wide range of personnel, from technicians to building occupants.
Clear visualizations and actionable reports are crucial for informed decision-making. The platform should also allow for customizability to meet the specific needs of different user roles.
Security and Data Privacy
Ensuring the security and privacy of data is paramount in a smart building environment. The platform must incorporate robust security measures to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and malicious attacks. This includes encryption protocols, access controls, and regular security audits to maintain a secure environment. Data privacy regulations should be adhered to, ensuring compliance with industry standards and user expectations.
Scalability and Maintainability
A smart building IoT platform needs to be scalable to accommodate the increasing number of devices and data points as the building evolves and expands. The platform architecture should be designed with scalability in mind, allowing for easy addition of new functionalities and devices without compromising performance or reliability. A well-structured platform architecture will ensure maintainability, making it easier to update, upgrade, and troubleshoot potential issues.
Maintainability also involves creating clear documentation and providing support resources to ensure long-term platform usability and effectiveness. A robust support system is essential for resolving issues and ensuring a seamless experience.
Interoperability and Open Standards
Interoperability between different systems and platforms is crucial for a truly integrated smart building. The platform should adhere to open standards and protocols to ensure seamless communication with other systems. This allows for greater flexibility and the ability to integrate with new technologies and systems in the future. Open standards foster innovation and promote the development of a rich ecosystem of connected devices and applications.
Adoption of open protocols facilitates the exchange of data between various platforms, fostering a more dynamic and adaptable building environment. This promotes long-term growth and ensures that the building can evolve with technology.
Future Trends and Innovations in Smart Building IoT Platforms

Emerging AI-Powered Solutions
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming various sectors, and its impact on software development is undeniable. AI-powered tools are automating tasks, improving code quality, and accelerating development cycles. AI can analyze vast amounts of code to identify patterns, predict potential bugs, and even generate code snippets, significantly boosting developer productivity.
Enhanced Cybersecurity Measures
With the increasing reliance on digital systems, cybersecurity is paramount. Future software development will prioritize robust security measures, incorporating advanced encryption techniques, threat detection systems, and proactive vulnerability assessments. Developers will need to be highly adept at building secure applications from the ground up. This includes understanding the latest attack vectors and implementing safeguards to protect user data and prevent breaches.
Cloud-Native Development and Infrastructure
Cloud computing continues to evolve, and software development is increasingly adopting cloud-native architectures. This approach emphasizes building applications that are designed to run seamlessly across various cloud platforms. This trend is driven by the need for scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Developers will need expertise in cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud to successfully develop and deploy applications.
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing, a model where the cloud provider manages server infrastructure, is gaining significant traction. It enables developers to focus on application logic without managing servers, leading to increased efficiency and cost savings. The reduced operational overhead allows developers to concentrate on innovation and deliver features faster. This paradigm shift will redefine how software is developed and deployed.
Low-Code/No-Code Platforms
Low-code/no-code platforms are democratizing software development, making it accessible to a broader range of users. These platforms provide visual interfaces and pre-built components, allowing developers and non-developers to create applications with less coding. This approach simplifies development, enabling faster application delivery and reducing development costs. However, the need for skilled developers to maintain and scale these applications will remain critical.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
The Internet of Things (IoT) is rapidly expanding, connecting billions of devices. Future software development will need to address the unique challenges and opportunities presented by IoT. Developing secure, scalable, and reliable software solutions for managing and interacting with these connected devices will be crucial. Developers will need to create applications that can collect, process, and analyze vast amounts of data from diverse IoT devices.
Blockchain Technology Implementation
Blockchain technology is emerging as a disruptive force in various sectors, including software development. Its secure and transparent nature offers unique opportunities for creating trustless and auditable systems. Future software applications will incorporate blockchain to enhance security, improve transparency, and facilitate secure data exchange. The integration of blockchain into various aspects of software development will be a key area of innovation.
Read more about Smart Building IoT Platforms: Seamless Integration
Hot Recommendations
- Sustainable Real Estate Design Principles
- AI in Real Estate: Streamlining the Buying Process
- Climate Risk Disclosure: A Must for Real Estate
- Climate Risk Analytics: Essential for Real Estate Investment Funds
- Modular Sustainable Construction: Scalability and Speed
- Real Estate and Community Disaster Preparedness
- Smart Buildings and Advanced Building Analytics for Optimal Performance
- Smart Waste Sorting and Recycling in Buildings
- Sustainable Real Estate: A Strategic Advantage
- AI in Real Estate Transaction Processing: Speed and Accuracy