Modular Sustainable Housing: Future Trends
The Rise of Prefabricated Construction in Sustainable Housing
Prefabrication's Environmental Advantages
Prefabricated construction, often referred to as modular construction, is rapidly gaining traction as a key component in sustainable housing initiatives. The controlled factory environment allows for precise material utilization, minimizing waste and reducing the environmental footprint associated with traditional on-site construction. This meticulous approach to material management translates to significant savings in resources like timber, steel, and concrete, leading to a decreased carbon footprint throughout the entire building lifecycle. Furthermore, prefabrication often facilitates the use of recycled and renewable materials, further enhancing the sustainability profile of the project.
Reduced construction time on-site, a direct consequence of prefabrication, translates to less disruption to the surrounding environment. Fewer vehicles on-site, lower noise pollution, and minimized dust contribute to a more harmonious and sustainable construction process. The inherent precision of factory-produced components also leads to higher quality control and fewer construction errors, reducing the need for costly rework and material replacements, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable outcome.
Economic and Social Benefits of Prefabricated Housing
Beyond environmental benefits, prefabricated construction offers compelling economic and social advantages. The standardized nature of prefabricated components allows for streamlined production processes, often resulting in significant cost savings. This cost-effectiveness can make high-quality, sustainable housing more accessible to a broader range of individuals and communities. The efficient factory production process also enables faster construction times, allowing for quicker project turnarounds and potentially reducing the overall project costs compared to traditional construction methods.
Prefabrication fosters the development of skilled trades in the manufacturing sector, leading to job creation and economic growth in areas focused on sustainable construction. This specialized workforce can contribute to a stronger, more sustainable future by creating jobs and expertise in the sustainable construction sector. Furthermore, the enhanced quality control in the factory setting translates to improved building performance, durability, and energy efficiency, ultimately leading to long-term cost savings for homeowners.
The modular nature of prefabricated homes also allows for greater flexibility in design and customization. Different modules can be assembled in various configurations, catering to diverse needs and preferences. This adaptability fosters more sustainable housing solutions that can be tailored to specific site conditions and customer requirements, minimizing waste and maximizing the utilization of resources.
Prefabrication also plays a crucial role in addressing housing shortages in many areas. Faster construction times and standardized processes enable the rapid delivery of more homes, which can have a significant impact on communities facing housing challenges. This rapid deployment contributes to the reduction of housing waiting lists, thereby easing the pressure on local housing markets.
The increased use of prefabricated construction methods in sustainable housing is a clear indication of a positive trend. The combination of environmental benefits, economic advantages, and social contributions makes it an attractive and promising approach to building a more sustainable future.
Key Drivers Behind the Demand for Modular Sustainable Homes

Technological Advancements
The rapid evolution of technology plays a pivotal role in shaping consumer demand. Innovative products and services, driven by advancements in areas like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation, are constantly emerging. These advancements often lead to new possibilities and functionalities, creating a need for consumers to adopt these technologies and improve their lives. This continuous cycle of innovation fuels demand for a wide range of goods and services, pushing the boundaries of what's possible.
Economic Factors
Economic conditions significantly influence consumer spending and, consequently, demand. Factors such as inflation, interest rates, and economic growth directly impact purchasing power. When economic conditions are favorable, consumers tend to feel more confident and spend more, leading to higher demand. Conversely, economic downturns can lead to decreased consumer spending and lower demand.
Demographic Shifts
Population growth, aging populations, and changing demographics are all important factors influencing consumer demand. Shifting demographics bring with them varying needs and wants that drive demand for goods and services tailored to specific age groups, ethnicities, and lifestyles. Understanding these demographic trends is crucial for businesses to anticipate and meet the evolving needs of their target markets.
Social and Cultural Trends
Social and cultural trends are powerful drivers of demand. Changing social values, preferences, and attitudes toward various products and services greatly impact purchasing decisions. For example, the growing emphasis on sustainability and ethical consumption is influencing consumer choices, leading to a higher demand for eco-friendly products and services. The increasing prevalence of social media also plays a significant role in shaping trends and influencing consumer behavior.
Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations can have a profound impact on consumer demand. Policies related to taxation, subsidies, and trade agreements all affect the price and availability of goods and services. Regulations related to product safety and environmental protection can influence consumer choices and demand for certain products. Understanding the interplay between government policies and consumer demand is essential for businesses to adapt and thrive.
Global Events and Crises
Global events, such as pandemics, political instability, and economic crises, can significantly impact consumer demand. Disruptions to supply chains, changes in consumer confidence, and shifts in priorities can all have a substantial effect. Events like the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the importance of resilience and adaptability in the face of global shocks. These events can create both short-term and long-term shifts in consumer behavior and demand.
Innovative Materials and Design for Sustainable Modular Homes

Advanced Polymer Composites
Polymer composites are revolutionizing various industries by combining the desirable properties of polymers with those of other materials. This synergistic approach leads to materials with enhanced strength, stiffness, and durability, while often reducing weight compared to traditional materials. These composites are finding increasing applications in aerospace, automotive, and construction sectors, where lightweight yet robust components are crucial.
The development of advanced polymer matrices and carefully selected reinforcement fillers is critical. This meticulous process ensures the creation of materials with optimized mechanical properties tailored to specific applications. The ability to tune the composite's characteristics is a major driving force behind their growing popularity.
Nanomaterials Integration
Nanomaterials, with their unique properties at the nanoscale, are opening up exciting possibilities for material design. Their incorporation into existing materials can significantly enhance their performance, leading to breakthroughs in areas like energy storage, electronics, and biomedical devices. The enhanced surface area and unique interactions at the nanoscale enable new functionalities.
For example, incorporating nanoparticles into polymer matrices can improve their electrical conductivity, thermal stability, and mechanical strength. These improvements can create innovative solutions for demanding applications.
Bio-Inspired Designs
Drawing inspiration from nature's ingenious designs has led to the creation of bio-inspired materials and structures. This approach leverages the inherent efficiency and effectiveness of natural forms to develop novel solutions. Mimicking the structures and mechanisms of biological systems can unlock new possibilities in material science.
For instance, the hierarchical structures found in bone, wood, and other biological materials offer clues for designing stronger and lighter composite materials. These bio-inspired designs often result in materials with superior performance characteristics.
Sustainable Material Choices
The increasing focus on sustainability is driving the exploration of eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes. This includes the use of bio-based polymers, recycled materials, and the development of more sustainable production methods. These sustainable choices are crucial for minimizing the environmental impact of the materials and manufacturing process.
3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
3D printing and additive manufacturing techniques offer unprecedented opportunities for creating complex and customized components. This technology allows for the fabrication of intricate shapes and structures that were previously impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. The ability to design and produce complex geometries opens up new possibilities for tailoring materials to specific needs.
Smart Materials and Self-Healing
Smart materials, which respond to external stimuli, are transforming numerous applications. These materials can adapt to changing conditions, leading to enhanced performance and durability. Self-healing materials, inspired by biological systems, are a particularly promising area of research.
These materials can automatically repair themselves when damaged, extending their lifespan and reducing maintenance costs. These advances are paving the way for more resilient and long-lasting structures and components.
Advanced Manufacturing Processes
Advanced manufacturing processes are essential for realizing the full potential of innovative materials. Techniques such as high-pressure molding, nano-imprint lithography, and advanced thermal treatments are critical for achieving the desired material properties and ensuring high-quality components. These sophisticated processes are vital for transforming innovative materials into robust and reliable products.
Future Trends and Technological Advancements
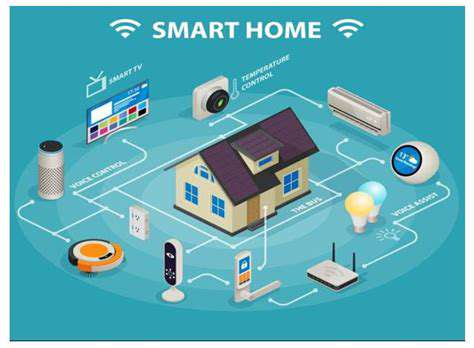
Smart Home Integration
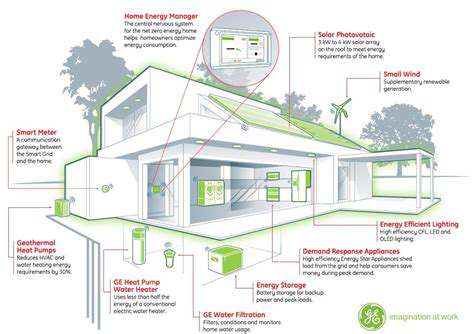
The integration of smart home technology into modular sustainable housing is poised to revolutionize the residential experience. Imagine a home that anticipates your needs, automatically adjusting lighting, temperature, and security based on your schedule and preferences. This level of automation not only enhances comfort and convenience but also contributes to energy efficiency by optimizing resource consumption. Smart appliances and energy management systems can monitor and adjust energy usage in real-time, leading to significant cost savings and a reduced carbon footprint. This integration is increasingly important for the future of sustainable living, providing a more responsive and environmentally conscious approach to housing.
Furthermore, smart home systems can facilitate remote monitoring and maintenance. This is particularly beneficial for homeowners who live in different locations or for those who require assistance with daily tasks. The ability to remotely control and monitor systems, such as security cameras and environmental sensors, enhances safety and allows for proactive maintenance, minimizing unexpected issues and ensuring the longevity of the modular structure.
Advanced Material Innovations
The development of new, sustainable, and high-performance materials will play a crucial role in shaping the future of modular sustainable housing. Researchers are exploring innovative composites, bio-based materials, and recycled plastics to create lightweight, durable, and environmentally friendly building components. These advancements will not only reduce the environmental impact of construction but also improve the overall structural integrity and aesthetic appeal of modular homes.
These advancements in materials science are essential for achieving the ambitious goals of sustainability. By employing lighter, stronger materials, builders can reduce the amount of raw material needed, minimizing the environmental footprint associated with extraction and processing. The use of recycled materials further enhances the circular economy, creating a truly sustainable building process. The exploration of advanced materials is a critical component in ensuring the long-term viability and environmental responsibility of modular housing.
Modular Construction Efficiency
The ongoing evolution of modular construction techniques will significantly impact the speed and efficiency of housing production. Automation and prefabrication will allow for the construction of homes in factory settings, leading to faster production cycles and reduced on-site labor costs. This approach not only optimizes the building process but also minimizes waste and construction-related emissions.
This increased efficiency will also contribute to a more affordable housing market. By streamlining the construction process, builders can reduce overhead costs, making modular sustainable housing more accessible to a wider range of buyers. This cost-effectiveness, coupled with the environmental benefits, makes modular construction a key component in addressing the global housing crisis while promoting sustainability. Furthermore, prefabrication allows for greater precision and quality control in the production of housing components, leading to higher structural integrity and durability.
Sustainable Energy Integration
The incorporation of innovative renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, within modular sustainable housing will be a key trend. These systems, integrated into the building design, can generate clean energy on-site, reducing reliance on traditional grid power and minimizing the home's carbon footprint. This integration of renewable energy sources is crucial for creating truly sustainable and self-sufficient housing.
Furthermore, the design of modular homes can be optimized to maximize energy efficiency. Strategies such as passive solar design, high-performance insulation, and optimized ventilation can significantly reduce energy consumption, leading to lower utility bills and a smaller environmental impact. These combined strategies create a truly sustainable and cost-effective housing model.
Read more about Modular Sustainable Housing: Future Trends
Hot Recommendations
- Sustainable Real Estate Design Principles
- AI in Real Estate: Streamlining the Buying Process
- Climate Risk Disclosure: A Must for Real Estate
- Climate Risk Analytics: Essential for Real Estate Investment Funds
- Modular Sustainable Construction: Scalability and Speed
- Real Estate and Community Disaster Preparedness
- Smart Buildings and Advanced Building Analytics for Optimal Performance
- Smart Waste Sorting and Recycling in Buildings
- Sustainable Real Estate: A Strategic Advantage
- AI in Real Estate Transaction Processing: Speed and Accuracy