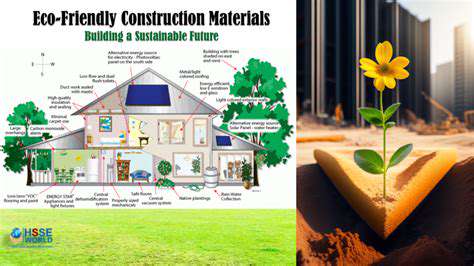
Carbon Sequestration in Green Building Materials
Bio-based materials, derived from plants, algae, and microorganisms, provide a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based products. Their production typically consumes less energy, resulting in lower carbon footprints. These materials are often biodegradable, reducing waste and supporting a circular economy.
Adopting bio-based materials across industries—from packaging to construction—is a significant step toward sustainability. Their renewability and biodegradability make them a compelling solution to mitigate the environmental harm caused by conventional materials. Continued research and development are needed to improve their performance and competitiveness.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) Technologies
CCS technologies capture CO2 emissions from industrial sources and store them underground, preventing atmospheric release. This approach is vital for achieving carbon neutrality, especially in hard-to-decarbonize sectors.
Various CCS technologies are in development, each with unique benefits and challenges. Scalability and effectiveness are critical for meeting global climate targets. However, long-term storage safety and leakage risks necessitate strict monitoring and regulations.
Synergy Between Bio-Based Materials and Carbon Capture
Combining bio-based materials with carbon capture offers a promising path to sustainability. Using bio-based feedstocks reduces fossil fuel reliance, while capturing emissions minimizes environmental impact. This creates a closed-loop system where material disposal also sequesters carbon.
Integrating these strategies fosters a circular economy, maximizing resource efficiency and minimizing waste. Success depends on innovative technologies and policies that incentivize sustainable practices.
The Role of Policy and Incentives
Government policies are crucial for promoting bio-based materials and CCS. Tax credits, subsidies, and regulations can drive innovation and investment. Carbon pricing mechanisms, like taxes or cap-and-trade systems, make CCS more viable.
Clear regulatory frameworks are essential to accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy. Collaboration between industries, researchers, and policymakers is key, as is international cooperation.
Advanced Composites and Carbon Capture Technologies
Advanced Materials for Carbon Capture
Advanced composites, such as carbon fiber, are vital for efficient carbon capture infrastructure. Their strength-to-weight ratio reduces material use, lowering costs and environmental impact. Corrosion and heat resistance ensure long-term reliability.
Material selection is tailored to operational conditions, ensuring optimal performance in diverse environments.
Carbon Capture Membranes: A Novel Approach
Innovative membrane technology enables efficient CO2 separation from flue gases. Advanced polymer composites with high permeability and selectivity are key to reducing energy use and scaling carbon capture.
Carbon Nanomaterials for Enhanced Adsorption
Carbon nanotubes and graphene offer high surface areas for CO2 adsorption, improving capture efficiency. Their modifiable surfaces allow customization for specific applications.
Process Integration and Optimization
Seamless integration of advanced materials and carbon capture into industrial processes is essential. Optimization focuses on energy efficiency, cost, and scalability to minimize environmental impact.
Economic and Policy Considerations
Economic viability drives widespread adoption. Government incentives and cost-benefit analyses are crucial. Evaluating material costs, manufacturing, and energy use alongside environmental benefits guides policy and investment.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Carbon Sequestration Strategies
Geological Sequestration: Deep Underground Storage
Geological sequestration stores CO2 underground in porous rock formations. Site selection and monitoring are critical to prevent leaks and ensure long-term stability. Regulatory frameworks must address these challenges while promoting responsible development.
Biological Sequestration: Enhancing Natural Processes
Afforestation, reforestation, and improved land management boost natural CO2 absorption. However, land use conflicts and biodiversity impacts require careful planning. Climate change effects on carbon sinks must also be considered.
Technological Advancements: Enhancing Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
Innovations in CO2 capture, transport, and storage improve efficiency and reduce costs, making sequestration more accessible to industries.
Social and Economic Considerations: Public Acceptance and Infrastructure Needs
Public support is vital. Transparent communication and stakeholder engagement build trust. Robust infrastructure and financing mechanisms are necessary for large-scale projects.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks: Incentives and Standards
Strong policies, carbon pricing, and clear regulations are essential to drive investment and ensure environmental protection.
Monitoring and Evaluation: Ensuring Long-Term Effectiveness
Comprehensive monitoring tracks CO2 storage and environmental impact, ensuring project success and safety.
The Future of Carbon-Negative Construction: A Sustainable Vision

The Rise of Carbon Capture Technologies
Carbon capture technologies are advancing rapidly, offering solutions to cut emissions. Widespread adoption could significantly reduce our carbon footprint. Direct air capture (DAC) shows particular promise for achieving net-zero goals.
Carbon-Negative Agriculture and Forestry
Sustainable farming and forestry enhance carbon sequestration. No-till farming and agroforestry store carbon in soil and vegetation, while forest protection and reforestation amplify natural carbon sinks.
Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS)
BECCS combines biomass energy with carbon storage. It has potential for net-negative emissions, but sustainable biomass sourcing and secure storage are critical.
Advanced Materials and Manufacturing
Lightweight, durable materials reduce energy use in transportation and industry. Sustainable manufacturing processes minimize waste and emissions. These innovations drive both environmental and economic benefits.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
Government policies, carbon pricing, and international cooperation are essential. Clear regulations and incentives spur investment and ensure equitable resource distribution.
Public Awareness and Engagement
Educating the public and promoting eco-friendly choices are vital. Community involvement in sustainability initiatives fosters collective action for a carbon-negative future.