Assessing Climate Risk in Residential Real Estate
Introduction to Climate Risk Assessment in Real Estate
Understanding the Fundamentals of Climate Risk
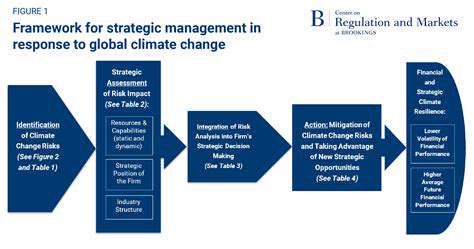
Climate risk assessment in real estate requires careful examination of how environmental hazards could influence property valuations, operational expenses, and investment performance. This process extends far beyond simple weather observations, incorporating complex future scenarios like coastal inundation, severe storms, and shifting rainfall distributions. Property professionals must grasp these elements to make sound decisions, allowing them to minimize exposure while identifying promising opportunities.
A thorough evaluation considers multiple climate variables, not just temperature fluctuations. It demands expertise in regional climate forecasts, including expected variations in precipitation, thermal extremes, and storm behavior. Such insights prove indispensable for judging long-term property viability and crafting appropriate resilience measures.
Spotting Potential Climate Threats
Recognizing environmental hazards forms the foundation of effective assessment. Professionals examine past climate records to detect trends, then apply predictive models to anticipate future challenges. Locations susceptible to inundation or wildfires warrant particular attention, while projections of intensified cyclonic activity or arid conditions significantly affect real estate valuation.
Detailed hazard analysis must account for potential consequences to specific properties, surrounding infrastructure, and community networks. This granular approach pinpoints vulnerable assets and informs tailored risk reduction tactics.
Assessing Property Vulnerabilities
Following hazard identification, analysts evaluate how individual properties might be affected. This involves scrutinizing physical characteristics including geographic placement, construction quality, and architectural design. For instance, waterfront developments face greater exposure to oceanic encroachment than inland sites, while aging structures often demonstrate reduced capacity to withstand extreme conditions.
Formulating Resilience Strategies
Developing adaptive measures represents a critical phase of climate risk evaluation. These solutions aim to reduce property susceptibility and limit potential damages. Options include flood prevention systems, enhanced building standards for weather resistance, or robust infrastructure development. Customized adaptation plans should address specific environmental threats facing both individual properties and their communities.
Incorporating Climate Factors into Investment Analysis
Integrating environmental considerations into real estate decisions ensures sustainable market performance. By factoring climate projections and vulnerability studies into investment evaluations, stakeholders can avoid costly pitfalls. This process examines potential devaluation risks, escalating insurance premiums, and operational interruptions. A sophisticated understanding of climate threats helps investors recognize sustainable opportunities with strong resilience characteristics.
Identifying Potential Climate Hazards
Understanding Climate Change Impacts
Environmental transformation now presents immediate challenges rather than distant concerns. Global temperature increases, altered rainfall distributions, and more frequent severe weather events already damage infrastructure and affect public welfare. Recognizing these localized effects proves essential for evaluating residential property risks and designing appropriate response measures.
Examining Precipitation Changes
Shifting rainfall patterns featuring heavier downpours and prolonged dry spells can trigger flooding, slope failures, and water shortages. Reviewing historical precipitation records alongside future forecasts helps determine event probability and potential severity for specific locations. This examination proves vital for assessing property resistance to water-related damage.
Assessing Thermal Extremes
Rising temperatures threaten residential properties through increased cooling demands and accelerated infrastructure deterioration. Evaluating heat wave duration and frequency helps predict impacts on home values and regional habitability. Detailed thermal analysis forms a critical component of comprehensive risk assessment.
Analyzing Severe Weather Patterns
More frequent and intense hurricanes, tornadoes, and wildfires can devastate residential properties. Studying historical storm data including intensity metrics, duration, and trajectories helps estimate potential damage. Special attention should focus on projected wind speed increases and coastal storm surges.
Evaluating Coastal Inundation Risks
Shoreline communities confront substantial threats from oceanic encroachment causing erosion, saline intrusion, and flooding. Examining sea-level projections while considering local factors like land subsidence proves essential for assessing property damage potential.
Inspecting Infrastructure Vulnerabilities
Existing residential systems including plumbing, electrical networks, and foundational elements may prove susceptible to climate effects. Evaluating infrastructure resilience to thermal stress and extreme weather helps predict failure risks. Transportation network durability assessments also contribute to regional resilience evaluations.
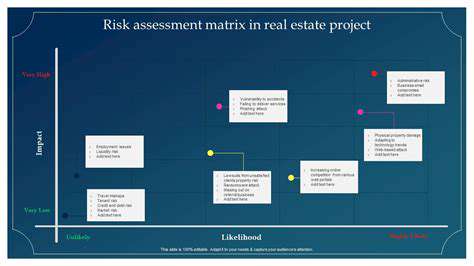
Analyzing the Likelihood and Severity of Hazards
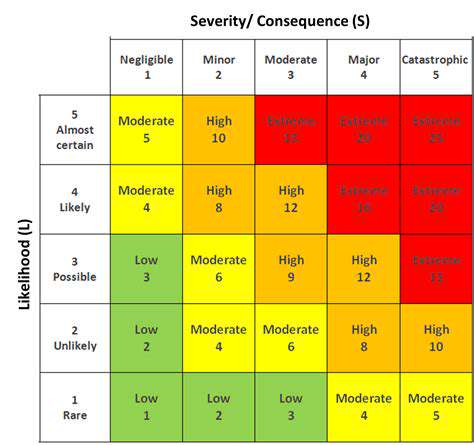
Calculating Event Probability
Determining event probability forms the cornerstone of risk analysis. This process examines contributing elements, reviews historical precedents when available, and assesses recurrence patterns. Comprehensive factor analysis must consider contextual relationships and manifestation probabilities for each component.
Measuring Potential Consequences
Following probability assessment, impact evaluation examines potential financial, operational, and reputational effects. This comprehensive review considers outcomes ranging from minor disruptions to catastrophic failures. Quantifiable impact measurement facilitates effective risk control strategies.
Synthesizing Probability and Impact
Effective risk management emerges from understanding probability-impact relationships. High-probability, low-impact events may warrant preventive actions, while low-probability, high-impact scenarios could require contingency planning. Strategic risk prioritization combines both dimensions to optimize resource allocation.
Practical Strategies for Mitigation and Adaptation
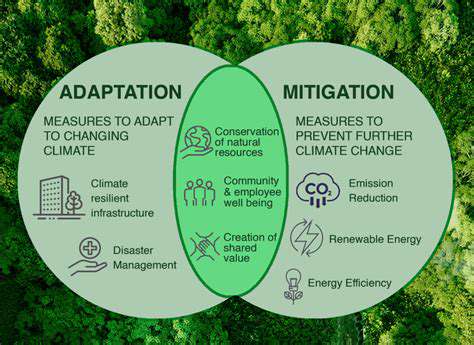
Investigating Underlying Causes
Successful mitigation approaches originate from deep understanding of fundamental issues rather than surface symptoms. Root cause analysis examines historical context, environmental factors, and systemic weaknesses to develop durable solutions.
Establishing Preventive Measures
Proactive strategies build system resilience through preventative maintenance, enhanced safety protocols, and organizational awareness. Forward-looking investments often prove more economical than reactive solutions following crisis events.
Creating Response Plans
Contingency blueprints outline specific crisis response actions, ensuring organizational preparedness. Regular plan reviews maintain alignment with evolving conditions and threat landscapes.
Implementing Performance Tracking
Monitoring systems collect strategy implementation data, enabling continuous improvement. Timely data analysis identifies effectiveness trends and adjustment requirements.
Optimizing Resource Distribution
Strategic resource allocation balances financial and human capital against priorities. Clear resource management prevents conflicts and aligns team efforts.
Fostering Organizational Cooperation
Effective mitigation requires transparent communication among stakeholders. Collaborative environments enhance problem-solving and solution implementation.
Read more about Assessing Climate Risk in Residential Real Estate
Hot Recommendations
- Sustainable Real Estate Design Principles
- AI in Real Estate: Streamlining the Buying Process
- Climate Risk Disclosure: A Must for Real Estate
- Climate Risk Analytics: Essential for Real Estate Investment Funds
- Modular Sustainable Construction: Scalability and Speed
- Real Estate and Community Disaster Preparedness
- Smart Buildings and Advanced Building Analytics for Optimal Performance
- Smart Waste Sorting and Recycling in Buildings
- Sustainable Real Estate: A Strategic Advantage
- AI in Real Estate Transaction Processing: Speed and Accuracy