Real Estate Due Diligence: Incorporating Climate Risk Factors
Incorporating Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies

Understanding the Scope of Climate Change Mitigation
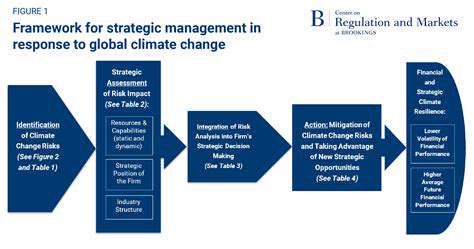
Climate change mitigation encompasses a wide range of actions aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions and lessening the severity of future climate change impacts. This involves transitioning to cleaner energy sources, improving energy efficiency in buildings and transportation, and promoting sustainable land use practices. Understanding the scope of this challenge is crucial for developing effective and comprehensive strategies. This requires a holistic approach that considers the interconnectedness of various sectors of the economy and society.
Technological Advancements in Mitigation
Significant technological advancements are crucial for mitigating climate change. Renewable energy technologies like solar and wind power are rapidly improving in efficiency and cost-effectiveness, making them increasingly viable alternatives to fossil fuels. Innovations in carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies hold promise for reducing emissions from existing industrial processes. These advancements are paving the way for a more sustainable future but require significant investment and policy support.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks for Mitigation
Effective climate change mitigation relies heavily on robust policy and regulatory frameworks. These frameworks need to incentivize the adoption of cleaner technologies and practices, while disincentivizing the continued reliance on fossil fuels. Carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems, can create economic signals that drive emissions reductions. International cooperation and agreements are essential to address the global nature of the climate challenge.
Sustainable Practices in Transportation
The transportation sector is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. Shifting towards sustainable transportation options, such as electric vehicles, public transportation, and cycling infrastructure, is crucial for mitigating climate change. Implementing policies that encourage the adoption of electric vehicles and incentivize the use of public transportation are vital steps in this direction. Promoting active transportation, like walking and cycling, can also significantly reduce emissions and improve public health.
Sustainable Energy Solutions for Homes and Businesses
Energy efficiency improvements in homes and businesses are crucial for reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Implementing energy-efficient building codes, promoting the use of renewable energy sources for heating and cooling, and supporting the development of smart grids are important steps. These initiatives can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of residential and commercial buildings. Investing in energy-efficient appliances and technologies can further contribute to the reduction of emissions.
Sustainable Land Use and Agriculture
Sustainable land use practices, such as reforestation, afforestation, and sustainable agriculture, play a critical role in mitigating climate change. Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing significant amounts of atmospheric carbon dioxide. Sustainable agricultural practices can reduce emissions from agricultural activities and enhance the ability of land to sequester carbon. Protecting and restoring natural ecosystems is vital for maintaining biodiversity and supporting climate resilience.
International Cooperation and Global Action
Climate change is a global challenge that requires international cooperation and global action. International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, provide a framework for countries to work together to reduce emissions. Sharing knowledge, technology, and resources among nations is essential for accelerating the transition to a low-carbon economy. Financial support and capacity building for developing countries are also crucial for their participation in global mitigation efforts.
Read more about Real Estate Due Diligence: Incorporating Climate Risk Factors
Hot Recommendations
- Sustainable Real Estate Design Principles
- AI in Real Estate: Streamlining the Buying Process
- Climate Risk Disclosure: A Must for Real Estate
- Climate Risk Analytics: Essential for Real Estate Investment Funds
- Modular Sustainable Construction: Scalability and Speed
- Real Estate and Community Disaster Preparedness
- Smart Buildings and Advanced Building Analytics for Optimal Performance
- Smart Waste Sorting and Recycling in Buildings
- Sustainable Real Estate: A Strategic Advantage
- AI in Real Estate Transaction Processing: Speed and Accuracy