Community Scale Sustainable Real Estate Projects
Defining Community-Scale Sustainability
Defining Community-Scale Sustainability
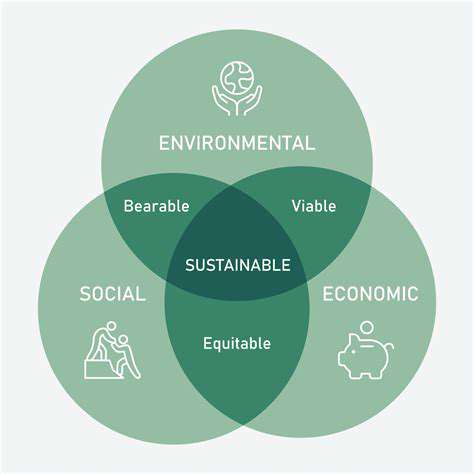
Community-scale sustainability represents a comprehensive strategy for building thriving and resilient neighborhoods. Rather than focusing solely on individual efforts, it emphasizes the collective welfare of a community, integrating environmental preservation, social equity, and economic stability. This interconnected framework acknowledges that progress in one domain frequently depends on advancements in others, creating a web of mutually reinforcing benefits.
Foundational to this approach is crafting tailored solutions that respond to each community's distinct characteristics. These strategies should flex to accommodate local assets, population dynamics, and cultural traditions. Lasting solutions emerge from grassroots involvement, equipping residents to shape policies and implement changes that directly affect their lives.
Environmental Stewardship
Environmental responsibility at the community level centers on shrinking ecological impacts through practical measures. Initiatives might include comprehensive recycling systems, expanded public transit options, and support for regional agriculture. Eco-conscious practices in these areas form the bedrock of enduring community vitality.
Successful environmental programs typically combine awareness campaigns with hands-on participation opportunities. Educating residents about conservation techniques while providing accessible ways to implement them cultivates widespread ecological responsibility.
Social Cohesion
Building inclusive societies where all members feel valued requires intentional effort toward fairness and justice. This encompasses designing universally accessible public spaces, nurturing neighborhood connections, and encouraging cooperative problem-solving for social challenges.
Community investment in educational and vocational programs creates pathways for residents to flourish while strengthening the social fabric. Educational opportunities and supportive networks function as cornerstones for durable communities. Shared purpose and interpersonal connections remain vital for maintaining unity and ensuring collective prosperity.
Economic Resilience
Local economic health depends on cultivating enterprises that serve both profit motives and community needs. Prioritizing neighborhood businesses, generating meaningful employment, and developing commerce strategies that weigh social and environmental consequences all contribute to this balance. Farmers' cooperatives, artisan collectives, and similar ventures foster economic interdependence with community benefits.
Sustainable economic models emphasize employment that provides living wages while minimizing ecological harm. Equitable distribution of economic gains ensures broad access to opportunities and essential resources.
Governance Models
Thoughtful administration provides the scaffolding for community sustainability efforts. This includes instituting policies that encourage responsible practices, maintaining open decision-making processes, and facilitating cooperation among diverse stakeholders. Visionary leadership helps align community energies toward shared sustainable objectives, requiring both responsiveness to constituent needs and the ability to motivate collective effort.
Robust governance systems incorporate multiple perspectives through transparent processes, building trust and long-term commitment to sustainability initiatives.
Participatory Planning
Genuine sustainability requires active resident involvement in shaping community direction. Including community voices in planning and implementation ensures initiatives align with local priorities and values. This participatory approach fosters personal investment in outcomes, increasing the likelihood of sustained success. Meaningful resident engagement helps seamlessly incorporate sustainable practices into daily life.
Solutions developed through collaborative processes demonstrate greater effectiveness. Incorporating diverse viewpoints leads to more comprehensive and equitable resolutions to community challenges.
Essential Elements of Sustainable Neighborhood Design

Ecological Considerations
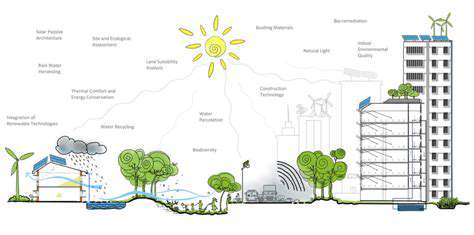
Environmental health remains fundamental to community sustainability. Safeguarding natural assets including woodlands, waterways, and ecosystems forms the basis for environmental equilibrium. Practical measures like waste reduction, energy conservation, and renewable power adoption help minimize human impact while preserving resources for coming generations.
Responsible land management and resource utilization represent critical components of environmental planning. Addressing pollution sources, improving waste processing infrastructure, and selecting sustainable construction materials all contribute to this effort.
Economic Foundations
Financial sustainability balances profitability with community welfare. This involves nurturing local commerce, developing employment pathways, and encouraging innovative enterprise. Sustainable economics prioritizes enduring community prosperity over temporary financial gains.
Economic resilience stems from diversity, reducing vulnerability to sector-specific downturns while encouraging organic growth across multiple areas.
Social Foundations
Equitable access forms the bedrock of healthy communities. Ensuring fair distribution of resources, services, and opportunities across all demographic groups promotes social harmony. This includes combating prejudice while guaranteeing educational access, healthcare availability, and housing security.
Community strength emerges from shared experiences and mutual support. Encouraging volunteer participation, backing local projects, and promoting cultural exchange all reinforce social bonds.
Administrative Framework
Effective governance structures support sustainable community evolution. Transparent decision protocols, meaningful public involvement, and balanced stakeholder representation characterize strong administrative systems. Quality leadership provides direction, manages assets, and builds agreement among competing interests.
Adaptable governance evolves with community needs, incorporating lessons learned and adjusting tactics to address new challenges.
Resident Involvement
Sustainable development thrives on active resident participation. Direct engagement in planning processes creates personal investment in community outcomes. This includes facilitating open discussion, creating feedback mechanisms, and establishing cooperative platforms.
Empowering residents to help mold their community's trajectory leads to more resilient and adaptive neighborhoods.
Technological Integration
Innovative technologies accelerate sustainable community progress. Strategic adoption of new systems can improve efficiency while reducing ecological strain. This includes exploring alternative energy options, implementing intelligent resource networks, and utilizing digital communication tools.
Advancements in waste processing, transportation, and food production systems offer significant sustainability improvements. Supporting research into environmentally-friendly technologies remains crucial for long-term success.
Cultural Continuity
Sustaining community identity through cultural preservation enriches neighborhood character. Honoring traditions and heritage strengthens communal identity and interpersonal connections. Supporting artistic expression, conserving historical landmarks, and encouraging cultural sharing all contribute.
Cultural preservation balances respect for tradition with thoughtful adaptation, intentionally weaving heritage values into contemporary development.
Technology and Innovation in Community Sustainability
Technological Solutions for Sustainability
Emerging technologies transform community infrastructure, offering novel approaches to sustainability challenges. Advanced energy networks optimize electricity distribution, decreasing waste while accommodating renewable sources. These integrated systems create more self-reliant community infrastructure with reduced dependence on centralized utilities. Water conservation technologies, including precision irrigation and advanced filtration, enable responsible usage – particularly critical in arid regions.
Sustainable mobility solutions demonstrate technology's environmental benefits. Electric transportation options combined with intelligent traffic coordination can dramatically lower emissions while improving urban air quality. These innovations support healthier lifestyles while reinforcing communal environmental commitment.
Collaborative Innovation for Community Development
Creative approaches to community cooperation strengthen collective sustainability efforts. Digital communication tools enable neighbors to coordinate recycling programs, urban agriculture projects, and conservation initiatives. These platforms enhance transparency while providing accessible participation channels.
Local innovation often targets specific community needs through tailored solutions. Citizen environmental monitoring programs, for example, engage residents in ecological data collection, informing community decision-making. This hands-on approach deepens environmental awareness while reinforcing communal responsibility.
Alternative funding models like community investment pools and microfinancing support sustainability projects while fostering shared ownership. These approaches democratize resource allocation and encourage broad participation.
Interactive environmental education programs build knowledge and skills for sustainable living. Practical workshops and digital learning tools equip residents to adopt eco-friendly habits and participate in conservation efforts.
Combining technological advancement with participatory approaches enables communities to create more resilient, equitable, and sustainable environments.

Read more about Community Scale Sustainable Real Estate Projects
Hot Recommendations
- Sustainable Real Estate Design Principles
- AI in Real Estate: Streamlining the Buying Process
- Climate Risk Disclosure: A Must for Real Estate
- Climate Risk Analytics: Essential for Real Estate Investment Funds
- Modular Sustainable Construction: Scalability and Speed
- Real Estate and Community Disaster Preparedness
- Smart Buildings and Advanced Building Analytics for Optimal Performance
- Smart Waste Sorting and Recycling in Buildings
- Sustainable Real Estate: A Strategic Advantage
- AI in Real Estate Transaction Processing: Speed and Accuracy