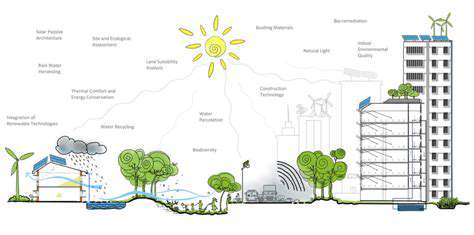
Sustainable Real Estate Development in Mixed Use

Integrating Green Building Materials and Practices
Choosing Eco-Friendly Materials
When constructing environmentally conscious buildings, the selection of sustainable building materials becomes paramount. Builders increasingly favor options with minimal embodied carbon - those demanding fewer resources for production. Recycled steel and certified sustainable timber offer compelling alternatives to virgin materials, dramatically lowering ecological footprints. The evaluation process must consider a material's complete lifecycle, from initial sourcing through eventual disposal, to ensure genuine sustainability.
Production methods significantly influence environmental impact. Environmentally responsible manufacturers employ renewable energy sources and implement water conservation measures during production. When selecting materials, professionals must balance ecological considerations with practical factors like cost and availability to make optimal choices.
Embracing Passive Design Strategies
Buildings designed with passive strategies dramatically reduce energy demands by harnessing natural elements. Thoughtful window placement, for instance, maximizes daylight while facilitating natural airflow, decreasing dependence on artificial lighting and mechanical cooling systems.
Proper building orientation and detailed site analysis form the foundation of effective passive design. By understanding seasonal sun patterns, architects can implement optimal shading solutions and window configurations. These approaches substantially lower operational energy requirements while enhancing occupant comfort through natural means.
Implementing Sustainable Construction Practices
Environmentally responsible construction extends beyond material selection to encompass the entire building process. Waste reduction initiatives, efficient debris management systems, and minimally invasive construction techniques all contribute to sustainable development.
Prefabrication offers multiple advantages, including reduced on-site waste and accelerated project timelines. Sourcing materials locally whenever feasible decreases transportation emissions while supporting regional economies. These practices collectively create more sustainable and economically viable construction projects.
Optimizing Energy Efficiency Systems
Advanced energy systems play a crucial role in sustainable buildings. High-performance insulation, energy-efficient windows, and modern HVAC systems significantly reduce operational energy consumption. Incorporating renewable energy sources, particularly solar panels, further decreases reliance on traditional power grids.
Building management systems (BMS) revolutionize energy optimization through real-time monitoring and adaptive control. These intelligent systems analyze usage patterns and environmental conditions to automatically adjust energy consumption, yielding substantial savings and carbon reduction.
Promoting Indoor Environmental Quality
Healthy indoor environments benefit both occupants and the planet. Low-VOC materials minimize airborne toxins, while natural ventilation and daylighting enhance air quality and reduce artificial lighting needs.
Advanced air purification systems and optimized ventilation strategies further improve indoor conditions. These measures simultaneously promote occupant health and support broader environmental sustainability goals through reduced energy consumption.
Promoting Transportation Efficiency and Accessibility

Optimizing Existing Infrastructure
Transportation system improvements begin with maximizing existing infrastructure potential. Comprehensive upgrades to road networks and public transit, combined with smart traffic management technologies, can dramatically improve efficiency. Real-time data analysis enables dynamic traffic adjustments, minimizing congestion and optimizing resource use across the transportation network.
Public transportation enhancements - including increased service frequency, expanded routes, and modernized stations - encourage greater ridership. These improvements reduce private vehicle dependence while creating more accessible, user-friendly transit options for all community members.
Encouraging Sustainable Transportation Practices
Active transportation modes like walking and cycling offer environmentally friendly alternatives for short trips. Strategic investments in bicycle infrastructure, including protected lanes and secure parking, significantly increase cycling adoption rates while promoting public health.
Carpooling initiatives and ride-sharing programs effectively reduce vehicle numbers on roadways. When combined with incentives for electric vehicle adoption and expanded charging infrastructure, these strategies collectively move communities toward sustainable mobility solutions. The cumulative impact creates cleaner, more efficient transportation systems that benefit both current and future generations.
Measuring and Monitoring Sustainability Performance
Establishing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Effective sustainability measurement begins with customized KPIs aligned with project-specific ESG objectives. Environmental metrics might track energy use intensity or renewable energy percentages, while social indicators could measure community engagement levels or workforce diversity. Early establishment of these metrics enables continuous progress evaluation throughout a project's lifecycle.
Tracking and Reporting Progress
Regular data collection and analysis form the backbone of meaningful sustainability measurement. Clear visualization tools like dashboards transform complex data into actionable insights for stakeholders. Transparent reporting builds trust while enabling continuous improvement through data-driven decision making.
Third-party verification enhances report credibility, while standardized measurement approaches across projects facilitate valuable benchmarking opportunities. Periodic KPI reviews ensure alignment with evolving sustainability standards and industry best practices.
Read more about Sustainable Real Estate Development in Mixed Use
Hot Recommendations
- Sustainable Real Estate Design Principles
- AI in Real Estate: Streamlining the Buying Process
- Climate Risk Disclosure: A Must for Real Estate
- Climate Risk Analytics: Essential for Real Estate Investment Funds
- Modular Sustainable Construction: Scalability and Speed
- Real Estate and Community Disaster Preparedness
- Smart Buildings and Advanced Building Analytics for Optimal Performance
- Smart Waste Sorting and Recycling in Buildings
- Sustainable Real Estate: A Strategic Advantage
- AI in Real Estate Transaction Processing: Speed and Accuracy