Insurability of Properties in High Risk Climate Zones
The Growing Threat of Climate Change Impacts on Property Insurance
Rising Premiums and Reduced Coverage
The escalating frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, like hurricanes, floods, and wildfires, are directly impacting property insurance markets. These events cause substantial damage to homes and businesses, leading to a surge in claims payouts. As insurers face increasing payouts and higher operational costs due to climate change, they are forced to raise premiums to maintain profitability. This rising cost of insurance can make it difficult for homeowners and businesses to afford coverage, potentially leading to a decline in the overall level of insured property.
Furthermore, insurers may reduce coverage limits or even decline to insure properties located in high-risk areas, exacerbating the problem. This creates a vicious cycle, where vulnerable populations are denied access to essential protection, and insurance companies face increasing financial strain. The result is a shrinking pool of insured properties, further complicating the ability of insurers to adequately price and manage risk.
Changes in Risk Assessment Models
Insurance companies are being forced to adapt their risk assessment models to account for the evolving climate patterns and the increasing frequency of extreme weather events. Traditional models often fail to accurately predict the impact of climate change on property values and potential damage. This necessitates significant revisions to incorporate factors such as sea-level rise, increased precipitation, and more frequent and intense heatwaves. The development of sophisticated models that accurately reflect these new realities is crucial for insurers to assess risk properly and set appropriate premiums.
Challenges in Mitigation and Adaptation
Property owners and communities are increasingly facing the challenge of mitigating the risks posed by climate change. Implementing measures such as flood-proofing homes, installing fire-resistant materials, and establishing effective drainage systems can help reduce vulnerability to extreme weather. However, these measures often come with significant upfront costs, and not all property owners have the financial resources to undertake them.
The Role of Government Intervention
Government policies and regulations play a critical role in addressing the growing threat of climate change impacts on property insurance. Regulations that incentivize climate-resilient construction, the development of building codes that consider climate change, and the provision of financial assistance to support mitigation efforts can help reduce the burden on both insurers and property owners. Government programs that provide disaster relief and support to affected communities are essential for helping those who have already suffered significant losses. Such policies are crucial for building a more resilient and equitable property insurance system.
The Future of Insurability
The future of property insurance in the face of climate change remains uncertain, but the trends point towards significant challenges and potentially disruptive changes. Insurers are likely to continue adjusting their pricing strategies and coverage options, potentially leading to a more complex and segmented insurance market. Furthermore, the need for government intervention to support mitigation efforts and ensure the availability of affordable insurance is likely to increase. Continued research, development, and collaboration between insurers, policymakers, and the public are essential for navigating these evolving challenges and ensuring the long-term sustainability of property insurance.
Factors Contributing to the Insurability Crisis

Economic Factors
Economic downturns and recessions often lead to increased unemployment and reduced consumer spending, which can negatively impact the overall health of the insurance industry. A decline in economic activity can decrease the demand for insurance products, particularly those related to property and casualty coverage. This is because consumers may postpone or cancel purchases due to financial constraints. This can also lead to a decrease in investment returns for insurers, impacting their profitability.
Conversely, periods of strong economic growth typically correlate with increased insurance demand. Robust business activity and higher consumer confidence often drive up need for various insurance products, from health to life to auto coverage. These factors, combined with higher investment returns, contribute to a more favorable environment for the insurance sector.
Demographic Shifts
Changes in population demographics, such as aging populations, increased life expectancy, and shifts in family structures, can significantly impact insurance needs. A growing elderly population often necessitates higher demand for long-term care insurance and other related coverage options. Also, the increasing prevalence of single-person households and later marriages may affect the demand for life insurance and related products.
Furthermore, migration patterns and urbanization contribute to changes in the risk profile of certain areas, influencing the pricing and availability of insurance products tailored to those locations. The changing demographics affect insurance needs in various ways, demanding adaptation from insurance providers.
Technological Advancements
Technological innovations are rapidly transforming the insurance landscape. The rise of big data, artificial intelligence, and machine learning has allowed insurers to better assess risk, personalize pricing, and automate processes. These advancements are leading to more efficient operations and potentially lower costs for consumers. Improved data analysis can lead to more accurate risk assessments and allow insurers to provide more tailored products and services.
Regulatory Environment
Government regulations and policies play a pivotal role in shaping the insurance industry. Regulations regarding premium pricing, claims handling, and investment strategies significantly impact the profitability and operations of insurance companies. Changes in these regulations can either create opportunities or challenges for insurance providers, sometimes leading to a need for significant adjustments in their business models.
Global Economic Interdependencies
Globalization and interconnectedness of global markets are influencing insurance markets in complex ways. Economic events in one part of the world can have a ripple effect on insurance markets globally, impacting investment opportunities and risk profiles. International trade agreements and political instability in various regions also create uncertainties for insurers. This means insurers need to consider global risks and opportunities in their strategies.
Consumer Behavior and Expectations
Consumer preferences and expectations regarding insurance products and services are constantly evolving. Consumers today are more informed and proactive in their insurance purchasing decisions. They are also seeking greater transparency, convenience, and personalized experiences from insurers. Consumers are also demanding more digital options and streamlined processes for claims filing and customer service. These changing consumer expectations require insurance providers to adapt their strategies to meet evolving demands.
Evaluating Risk and Implementing Mitigation Strategies
Understanding Property Risk Factors
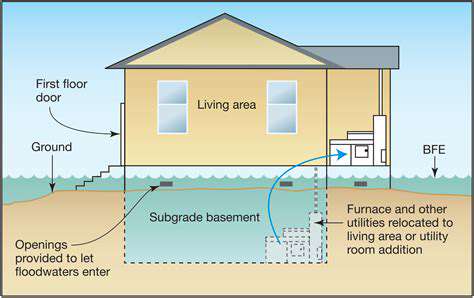
Assessing the inherent risks associated with a property is crucial for determining its insurability. These risks can stem from various sources, including environmental hazards like flooding, earthquakes, and wildfires, as well as structural deficiencies, historical damage records, and proximity to high-risk areas. Thorough inspections and analyses are essential to identify potential vulnerabilities and quantify the likelihood of different types of losses. Understanding these factors allows for a more accurate determination of the insurance premium and the appropriate level of coverage.
Geographical location plays a significant role in determining property risk. Areas prone to hurricanes, tornadoes, or other severe weather events will naturally carry a higher risk profile. Historical data on weather patterns and natural disasters in a particular region are valuable in evaluating this risk. Furthermore, the presence of hazardous materials on or near the property, or proximity to industrial facilities, can significantly increase the potential for unforeseen events and losses, impacting the cost of insurance.
Developing a Comprehensive Risk Assessment
A thorough risk assessment extends beyond simply identifying potential hazards. It involves a detailed analysis of the property's vulnerabilities, considering its construction, age, and potential for future damage. This comprehensive approach should also include an evaluation of the property's occupancy and use, as this can affect the likelihood of certain types of incidents. Understanding the potential for damage from vandalism, theft, or even internal issues like faulty wiring or plumbing is crucial to developing a complete picture of the risk profile.
Evaluating the financial impact of potential losses is a critical component of this assessment. Predicting the financial consequences of various scenarios, such as fire, flood, or structural collapse, allows property owners to make informed decisions about insurance coverage. Proper valuation of the property and its contents is essential for calculating the potential loss and determining the appropriate insurance limits. This process is essential for ensuring that the insurance policy adequately protects the investment.
Implementing Mitigation Strategies
Once the risk factors are identified, proactive mitigation strategies can be implemented to reduce the likelihood and impact of potential losses. These strategies may involve structural reinforcements, such as installing earthquake-resistant features or flood barriers. Implementing fire safety measures, such as smoke detectors and sprinklers, can significantly reduce the risk of fire damage. Regular maintenance and inspections of critical systems, including electrical and plumbing, are essential for preventing unforeseen breakdowns and their potential consequences.
Implementing effective security measures is another important mitigation strategy. These measures might include installing surveillance systems, reinforcing doors and windows, and implementing security protocols for access control. Furthermore, educating occupants about potential hazards and emergency procedures can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and injuries. These proactive steps can significantly lower the insurance premium and improve the overall safety of the property. Properly implementing these strategies can make a substantial difference in terms of both risk reduction and cost savings.
Insurance Policy Selection and Coverage
Once the risk assessment is complete and mitigation strategies are in place, the next step is to select an appropriate insurance policy. Different policies offer varying levels of coverage, and choosing the right one depends on the specific needs and risks of the property. Understanding the different types of coverage available, such as dwelling coverage, personal property coverage, and liability coverage, is critical. Careful consideration of the policy's exclusions and limitations is vital to ensure comprehensive protection against potential losses.
Negotiating the best possible terms with insurance providers is an essential part of the process. Comparing different policies and providers is crucial to finding the most cost-effective and comprehensive coverage. A thorough understanding of the policy's terms and conditions, including deductibles, coverage limits, and limitations, is essential to avoid any surprises or misunderstandings during a claim. This step ensures the property is adequately protected and the policy aligns with the property's unique risk profile.

Read more about Insurability of Properties in High Risk Climate Zones
Hot Recommendations
- Sustainable Real Estate Design Principles
- AI in Real Estate: Streamlining the Buying Process
- Climate Risk Disclosure: A Must for Real Estate
- Climate Risk Analytics: Essential for Real Estate Investment Funds
- Modular Sustainable Construction: Scalability and Speed
- Real Estate and Community Disaster Preparedness
- Smart Buildings and Advanced Building Analytics for Optimal Performance
- Smart Waste Sorting and Recycling in Buildings
- Sustainable Real Estate: A Strategic Advantage
- AI in Real Estate Transaction Processing: Speed and Accuracy