Flood Resilience in Real Estate: Case Studies
Elevated Structures: A Comprehensive Overview
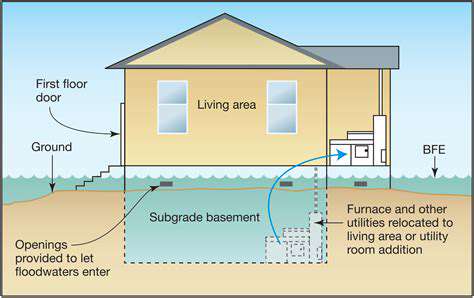
Modern elevated construction techniques have revolutionized flood-prone area development. Architects now design buildings that float during floods or rest on adjustable pylons. These innovative approaches preserve property values while maintaining neighborhood character in vulnerable coastal communities. The psychological impact of living above flood levels significantly improves resident peace of mind.
Material selection plays a crucial role in elevated construction. Marine-grade concrete and corrosion-resistant steel ensure longevity in humid, salt-rich environments. Proper elevation heights account for both current flood projections and anticipated sea level rise over the structure's lifespan.
Design Considerations for Elevated Structures
Elevated home designs must balance safety with livability. Architects incorporate flood vents that allow water passage without compromising structural integrity. Breakaway walls on lower levels prevent catastrophic failure during extreme events while preserving upper living spaces. Thoughtful designs often include convertible spaces that serve different functions before and during flood events.
Aesthetic integration remains paramount - elevated homes now feature design elements that blend with traditional neighborhood architecture. Creative landscaping helps conceal structural supports while providing additional drainage benefits.
Construction Techniques for Elevated Structures
Modern construction methods minimize neighborhood disruption during elevation projects. Hydraulic jacking systems can lift existing homes with remarkable precision. Prefabricated foundation components allow faster installation with consistent quality control. These advances have made elevation projects more accessible to middle-class homeowners through reduced labor costs.
Materials Used in Elevated Structures
Innovative composites now supplement traditional materials in elevated construction. Fiber-reinforced polymers offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios, while new waterproofing membranes protect vulnerable joints. Material scientists continue developing products that withstand prolonged water exposure without degradation.
Maintenance and Repair of Elevated Structures
Proactive maintenance preserves elevated home value and safety. Annual inspections should verify foundation integrity and check for corrosion. Homeowners benefit from establishing relationships with contractors experienced in elevated structure repairs. Proper maintenance records also help during insurance renewals and property sales.
Safety Regulations and Standards
Building codes for flood zones evolve alongside climate science. Current standards require elevation above base flood levels plus additional freeboard as a safety margin. Permitting processes now mandate engineering reviews to verify structural calculations for elevated designs. These measures ensure consistent safety across all flood-resistant construction.
Environmental Impact of Elevated Structures
Thoughtful elevation projects can enhance local ecosystems. Properly designed pilings create marine habitats, while elevated walkways protect sensitive dune vegetation. Some communities now require native plantings beneath elevated structures to maintain biodiversity and prevent erosion.
Retail channel integration presents complex operational challenges despite its advantages. Maintaining consistent brand presentation across diverse platforms requires meticulous content management systems and staff training protocols. Successful retailers invest in unified customer relationship platforms that synchronize data across all touchpoints in real time.
Case Study 3: Utilizing Nature-Based Solutions for Flood Mitigation
Understanding the Flood Risk
This valley community's flood history reveals patterns that inform current mitigation efforts. Detailed watershed modeling identified specific sub-basins contributing most to flash flood events. This analysis helped prioritize intervention areas where nature-based solutions could provide maximum benefit. Historical accounts from long-time residents supplemented technical data, revealing flood behaviors not captured in official records.
Economic impact studies quantified the true cost of recurrent flooding, including lost productivity and depreciated property values. These findings helped secure funding for mitigation projects by demonstrating their potential return on investment through reduced future damages.
Implementing Nature-Based Solutions
The community's phased implementation began with high-impact, low-cost interventions. Rain gardens installed in schoolyards doubled as outdoor classrooms while absorbing stormwater. Converted parking lots now feature permeable pavers that reduce runoff while maintaining functionality. Upstream wetland restoration projects help slow water flow before it reaches developed areas.
Volunteer programs engaged residents in solution implementation, creating local ownership of the projects. Training sessions taught proper planting techniques for native vegetation used in bioswales and riparian buffers. This hands-on involvement increased community understanding of how natural systems manage water.
Monitoring and Evaluation of Effectiveness
A network of stream gauges and soil moisture sensors provides quantitative performance data. Citizen scientists help maintain this equipment while learning about watershed hydrology. Before-and-after comparisons following storm events clearly demonstrate reduced peak flows in treated sub-basins. These measurable results build support for expanding the program.
Ecological monitoring tracks unintended consequences, ensuring solutions don't disrupt native species. Adaptive management protocols allow for mid-course corrections when monitoring reveals unexpected outcomes. This scientific approach has attracted research partnerships with local universities.
Community Engagement and Collaboration
The project's success stems from its inclusive planning process. Neighborhood charrettes generated creative solutions tailored to specific areas. Youth programs educated the next generation about watershed stewardship through hands-on projects. Local artists helped design interpretive signage that explains the natural systems at work.
Business partnerships created demonstration sites on commercial properties, showcasing how nature-based solutions can enhance curb appeal while providing functional benefits. These visible examples helped overcome initial skepticism about unconventional approaches.
Cost-Benefit Analysis and Sustainability
Lifecycle cost analyses revealed significant savings compared to traditional gray infrastructure. While initial installation costs were comparable, nature-based solutions require less expensive maintenance and have longer functional lifespans. The additional benefits of improved air quality, urban cooling, and recreational space added substantial value beyond flood reduction.
Ongoing endowment funds ensure proper long-term maintenance through a mix of municipal funding and conservation easements. This financial model guarantees the solutions will continue functioning as intended for decades to come.
Read more about Flood Resilience in Real Estate: Case Studies
Hot Recommendations
- Sustainable Real Estate Design Principles
- AI in Real Estate: Streamlining the Buying Process
- Climate Risk Disclosure: A Must for Real Estate
- Climate Risk Analytics: Essential for Real Estate Investment Funds
- Modular Sustainable Construction: Scalability and Speed
- Real Estate and Community Disaster Preparedness
- Smart Buildings and Advanced Building Analytics for Optimal Performance
- Smart Waste Sorting and Recycling in Buildings
- Sustainable Real Estate: A Strategic Advantage
- AI in Real Estate Transaction Processing: Speed and Accuracy