Beyond Flood Maps: Advanced Climate Risk Modeling for Property
Traditional float methods, while once a cornerstone of web design, often present significant challenges in maintaining layout stability. Their reliance on manual positioning and complex cascading can make it difficult to predict how elements will behave in different browser environments, especially as the complexity of a website increases. This inherent fragility can lead to unexpected layout shifts and visual inconsistencies across various devices and screen sizes, making it hard to guarantee a consistent user experience.
The manual intervention required often results in a less scalable and maintainable codebase, as adjustments to one element can have unforeseen consequences on others. Furthermore, the lack of inherent responsiveness can make websites difficult to adapt to different screen sizes, leading to poor mobile experiences and a diminished user satisfaction.
Grid-Based Solutions: Enhanced Control
Grid-based layouts offer a significant improvement over traditional float methods, providing a more structured and predictable approach to web design. Grid systems, such as CSS Grid Layout, offer an elegant solution by providing a more robust and intuitive means of aligning and arranging content. This structure, based on rows and columns, allows for greater control over the arrangement of elements, making it easier to achieve desired layouts and preventing the layout problems that frequently arise with floats.
Flexbox Flexibility: Adaptable Arrangements
Flexbox, another powerful CSS layout module, provides a flexible alternative to traditional methods. Its inherent ability to align items along a single axis (row or column) makes it particularly well-suited for responsive design. Flexbox grants developers the power to define how items behave within a container, offering precise control over their alignment, order, and distribution, all without the fragility associated with floats.
This adaptability translates to a more seamless and consistent user experience across different screen sizes and devices. The simplicity and power of flexbox allow for quick and efficient adjustments to layouts without the risk of introducing complex and unpredictable interactions.
Responsiveness and Media Queries: Adapting to Diverse Screens
Modern web design demands responsiveness. Traditional float methods often fall short in adapting to different screen sizes and resolutions, leading to distorted layouts or unusable interfaces. Media queries, a crucial component of responsive design, allow developers to target specific screen sizes and tailor the layout and styling accordingly. This approach ensures a consistent and usable experience across a wide range of devices, enhancing the user experience.
Accessibility Considerations: Improved User Experience
Accessibility is paramount in modern web design. Traditional float methods, with their inherent complexity and potential for layout inconsistencies, can create barriers for users with disabilities. Grid and flexbox layouts, with their structured nature, offer greater accessibility by providing better control over the flow and presentation of content. This translates into a more inclusive and user-friendly experience for everyone.
Scalability and Maintainability: Future-Proofing Designs
A well-structured design is vital for a long-lasting website. Traditional float methods can lead to complex and difficult-to-maintain codebases. Modern grid and flexbox layouts, with their inherent structure and predictable behavior, drastically improve scalability and maintainability. These approaches allow for easier updates and modifications, minimizing the risk of introducing bugs and improving the overall resilience of the website.
Integrating Climate Change Scenarios into Property Modeling

Understanding Climate Change Scenarios
Climate change scenarios are crucial for understanding the potential future impacts of global warming. These scenarios, developed by scientists, depict plausible future conditions based on different emission pathways and their associated environmental changes. They are not predictions, but rather portray a range of possible futures, allowing for a more holistic understanding of the challenges and opportunities ahead. This understanding is essential for developing robust and adaptive strategies to mitigate and manage the consequences of climate change.
These scenarios are vital for policymakers, researchers, and businesses, providing a framework for decision-making that considers the potential variability and uncertainty inherent in future climate projections. By exploring various potential futures, we can develop more effective and comprehensive strategies for addressing the impacts of climate change, including resource management, infrastructure planning, and adaptation measures.
Impact Assessment and Planning
One key application of climate change scenarios is in impact assessment. By modelling how different aspects of society and the environment might respond to various climate change scenarios, we can better understand the potential consequences of those changes. This includes evaluating the potential risks to human health, food security, water resources, and ecosystems.
Integrated assessment models, using climate change scenarios as input, enable us to quantify the potential economic impacts and allow for the evaluation of various adaptation strategies. This helps in prioritizing investments and resource allocation towards the most vulnerable areas and sectors. For example, scenarios can help predict how sea-level rise might affect coastal communities, enabling the development of protective measures.
Developing Adaptation Strategies
Climate change scenarios are essential for developing effective adaptation strategies. By understanding the range of possible future climates, we can develop more robust and resilient infrastructure and systems that can withstand the predicted impacts. This includes designing buildings that can withstand extreme weather events or developing drought-resistant crops.
Using climate change scenarios as a planning tool enables proactive measures. For instance, water management strategies can be developed to account for potential changes in rainfall patterns, and energy policies can be designed to support renewable energy sources in the face of shifting climate conditions. Such strategies are critical for minimizing risks and maximizing opportunities in a changing climate.
Policy and Decision-Making
Climate change scenarios are crucial for informing policy and decision-making at all levels, from local communities to international organizations. By providing a range of potential future outcomes, scenarios help policymakers evaluate the implications of different choices and prioritize actions that are most likely to lead to positive outcomes. This is particularly important in sectors like infrastructure development, where long-term planning is crucial.
The use of scenarios allows for a more comprehensive and holistic approach to policy formulation, going beyond short-term considerations and considering the potential impacts over extended periods. This allows for the development of more sustainable and resilient policies that address the challenges posed by climate change in a proactive and effective manner.
Communication and Engagement
Communicating climate change scenarios to diverse audiences is essential for fostering understanding and engagement. By presenting scenarios in a clear and accessible format, we can empower stakeholders to make informed decisions and take responsible actions. This includes translating complex scientific information into understandable narratives that resonate with the public.
Public engagement is crucial for building support for climate action. By connecting climate change scenarios to real-world impacts and potential consequences, we can foster a sense of shared responsibility and encourage individuals and communities to participate in mitigation and adaptation efforts. This includes communicating the potential benefits of acting on climate change, as well as the potential risks of inaction.
Valuing Property in a Changing Climate: Implications for Insurance and Investment

Understanding the Impact of Climate Change
Climate change is no longer a distant threat; its effects are being felt globally, impacting everything from agricultural yields to coastal communities. Understanding these impacts is crucial when assessing property value, as changing environmental conditions can significantly alter a property's desirability and long-term viability. This includes considering the potential for increased flooding, extreme weather events, and rising sea levels, all of which can dramatically reduce the value of certain properties.
Assessing Flood Risk and Mitigation Strategies
One of the most significant climate-related risks is flooding. Properties located in floodplains or areas prone to rising water levels may experience substantial devaluation. Evaluating the historical flood risk data for a property and considering the potential for future flooding scenarios are essential steps in the property valuation process. Mitigation strategies, such as flood defenses or elevation adjustments, can play a crucial role in increasing a property's value and resilience.
Evaluating the Impact of Extreme Weather Events
The increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, droughts, and wildfires, are reshaping property values. Properties located in high-risk areas may experience significant depreciation due to the increased likelihood of damage or disruption. Assessing the historical frequency and intensity of extreme weather events in a given location, along with the resilience of the property itself, is vital to understanding its valuation in a changing climate.
The Role of Rising Sea Levels in Coastal Valuation
Coastal areas are particularly vulnerable to the effects of rising sea levels. Erosion, saltwater intrusion, and increased storm surge are all factors that can drastically reduce the value of coastal properties. Valuations must account for the potential loss of land and access to the coastline, as well as the potential for increased maintenance costs associated with adapting to these changes.
Analyzing the Impact on Agricultural Land
Climate change is also significantly impacting agricultural land. Changes in temperature, precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events can all impact crop yields and livestock production. This, in turn, affects the long-term viability and value of agricultural properties. Evaluating the resilience of the land to these changes and the potential for adaptation strategies are critical considerations in agricultural property valuation.
Considering the Importance of Sustainable Practices
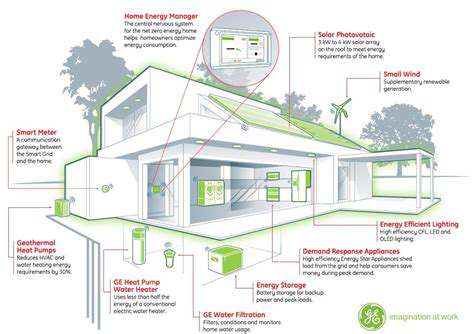
Properties that incorporate sustainable practices, such as energy efficiency measures, water conservation strategies, and green building materials, may command a higher value in a changing climate. These features demonstrate a proactive approach to environmental challenges and can attract buyers seeking environmentally conscious options. Analyzing these features is becoming increasingly important for accurate property valuations in a climate-conscious market.
The Future of Property Valuation in a Changing Climate
Property valuation in a changing climate requires a more holistic and forward-looking approach. This includes not only considering the current market conditions but also projecting potential future impacts, such as the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. Professionals need to adapt their methodologies to incorporate climate-related risks and opportunities into their assessments. This will lead to more accurate and reliable valuations that better reflect the true value of properties in the face of a changing climate.