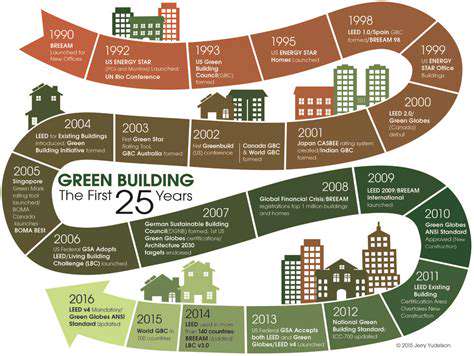
Net Zero Energy Buildings: Policy and Incentives
Economic Opportunities in a Sustainable Future
The transition to a net-zero economy presents significant economic opportunities. Investing in renewable energy technologies, sustainable infrastructure, and green technologies can create jobs and stimulate economic growth. The development of innovative solutions for carbon capture and storage, alongside the burgeoning demand for sustainable products and services, will foster new industries and markets. This shift can also lead to improved public health by reducing air pollution.
Companies that prioritize sustainability often attract environmentally conscious consumers and investors. This growing market demand for environmentally friendly products and services creates a strong incentive for businesses to adopt sustainable practices, fostering innovation and driving economic growth.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks for Net-Zero
Government policies and regulations play a critical role in driving the transition to a net-zero economy. These policies can incentivize investments in renewable energy, encourage energy efficiency, and establish carbon pricing mechanisms. Such frameworks are essential to create a level playing field for sustainable businesses and accelerate the adoption of clean technologies. Clear and consistent regulations are crucial for ensuring that the transition is fair and equitable.
International collaborations and agreements are essential for effectively tackling climate change. By working together, nations can share best practices, pool resources, and develop comprehensive strategies to achieve net-zero targets. This collective effort is critical for addressing the global nature of the climate crisis.
Technological Advancements Driving Progress
Technological advancements are accelerating the transition toward a net-zero future. Innovations in renewable energy technologies, such as solar and wind power, are becoming increasingly efficient and cost-effective. Furthermore, advancements in energy storage solutions are crucial for ensuring the reliability and stability of renewable energy systems. These advancements are making it possible to integrate renewable energy sources into the existing energy grid.
The development of carbon capture and storage technologies offers a crucial pathway to reducing emissions from industrial processes. Research and development in these areas will be vital for achieving net-zero goals in sectors with higher emissions. Continued investment in research and development will be essential for furthering these crucial advancements.
Policy Frameworks Supporting NZEB Development
Incentivizing NZEB Adoption
A crucial element in fostering the widespread adoption of Net-Zero Energy Buildings (NZEB) is the implementation of effective financial incentives. These incentives should not only encourage initial investments in energy-efficient technologies and design but also provide ongoing support for building operators to achieve and maintain NZEB performance. This could involve tax credits for materials and labor associated with NZEB construction, rebates for energy-efficient appliances and systems, and potentially even grants for energy audits and retrofits. Such policies create a positive feedback loop by encouraging innovation in the building sector and driving down the overall cost of NZEB construction over time, making them more accessible to a wider range of building owners and developers.
Furthermore, streamlined permitting processes and streamlined access to financing options tailored specifically to NZEB projects can significantly facilitate their development. Clearer and more consistent building codes and standards, along with simplified permitting procedures, reduce the administrative burden on developers and builders, allowing them to focus on the technical aspects of NZEB design and construction. Access to low-interest loans and specialized financing programs that recognize the unique financial aspects of NZEB projects can also significantly boost the adoption rate by making NZEB development more financially viable for a wider range of stakeholders.
Regulatory Frameworks and Standards
Establishing clear and comprehensive regulatory frameworks is essential for ensuring the consistent quality and performance of NZEB projects. These frameworks need to define specific energy performance targets, establish minimum standards for materials, and promote the use of advanced building technologies. Robust building codes and standards should incorporate NZEB principles, ensuring that new construction projects meet minimum energy efficiency requirements and promoting the adoption of sustainable design practices. This approach helps create a level playing field for developers, ensuring that all projects strive for high-performance standards.
Establishing clear and consistent standards for energy performance verification and certification is also crucial. A transparent and credible certification process assures both building owners and occupants that the building meets the NZEB criteria. This process should encompass rigorous testing and evaluation procedures to verify compliance and ensure that buildings are truly achieving net-zero energy performance. This robust framework fosters trust and confidence in the NZEB market, encouraging further investment and development.
Stronger enforcement mechanisms for code violations and a clear path for addressing performance issues after construction are also key components of a comprehensive NZEB policy framework. This ensures that builders and owners are held accountable for meeting the standards and that issues are addressed promptly, maintaining the integrity of the NZEB initiative. The overall goal is to foster a market where NZEB projects are not only viable but also consistently high-performing, contributing to a more sustainable built environment.
Incentives to Encourage NZEB Adoption
Financial Incentives: Rebates and Tax Credits
Governments can offer significant financial incentives to encourage the adoption of NZEB technology. These incentives can take the form of rebates for energy-efficient appliances, materials, and construction techniques. Offering tax credits for the upfront costs of NZEB construction can make the project more financially attractive to developers and homeowners. By lowering the initial investment barrier, these financial incentives can stimulate a greater market demand for NZEB solutions, fostering innovation and driving down the overall cost of net-zero energy construction over time.
Furthermore, targeted tax credits or deductions for ongoing energy savings achieved by NZEBs can incentivize building owners to maintain and optimize their energy performance. These incentives create a positive feedback loop, encouraging continuous improvement and driving the widespread adoption of energy-efficient practices.
Streamlined Permitting Processes
Complex and lengthy permitting processes can be a major deterrent to NZEB adoption. Simplification of building codes and streamlined permitting procedures can significantly reduce the bureaucratic hurdles faced by developers and homeowners. This can expedite the construction process, reduce costs, and ultimately increase the appeal of NZEBs.
Clearer guidelines and readily available resources for navigating the permitting process would ease the burden on stakeholders and encourage more widespread adoption of innovative net-zero energy solutions.
Energy Efficiency Standards and Codes
Mandatory energy efficiency standards and codes provide a crucial framework for NZEB adoption. These regulations set minimum requirements for energy performance, driving innovation and encouraging the development of more efficient building designs and technologies. Implementing stringent codes can ensure that new buildings meet specific energy efficiency criteria, contributing to a substantial reduction in overall energy consumption.
Public Awareness Campaigns and Education Initiatives
Raising public awareness about the benefits of NZEBs is essential for their widespread adoption. Educational campaigns can highlight the environmental and economic advantages of net-zero energy buildings, showcasing real-world examples and success stories. These initiatives can dispel misconceptions and promote a greater understanding of the benefits and opportunities associated with NZEB technology.
Policy Support for Research and Development
Government support for research and development (R&D) in NZEB technologies is crucial for accelerating innovation and driving down costs. Funding for research projects focused on advanced insulation materials, smart grids, and other cutting-edge technologies can lead to breakthroughs that make NZEBs even more efficient and cost-effective.
Investing in research and development not only promotes technological advancements but also strengthens the knowledge base for future generations of energy-efficient building professionals.
Incentives for Existing Building Retrofits
Focusing on retrofitting existing buildings to achieve net-zero energy standards is a crucial aspect of reducing the overall carbon footprint. Offering tax credits, grants, or financing options specifically for building retrofits can incentivize property owners to invest in energy efficiency upgrades. These incentives can create a significant positive impact, as retrofitting existing buildings often presents a more immediate opportunity for reducing energy consumption than constructing new buildings.
Collaboration and Partnerships
Fostering collaboration between government agencies, academic institutions, industry stakeholders, and the wider community is essential for successful NZEB adoption. Partnerships can facilitate the sharing of knowledge, resources, and best practices. Joint initiatives can help develop comprehensive strategies for implementing NZEB policies and driving innovation in the field.
Stronger partnerships lead to more comprehensive approaches to net-zero energy solutions, creating a more supportive ecosystem for the widespread adoption and implementation of NZEB technologies.
Challenges and Opportunities in Implementing NZEB Policies
Immediacy and Responsiveness
In today's fast-paced digital world, immediacy and responsiveness are paramount. Users expect instant gratification and seamless interactions. This demand for rapid access to information and services presents a significant challenge in ensuring the quality and accuracy of the content delivered. Meeting these expectations while maintaining high standards can be tricky, requiring a delicate balance between speed and thoroughness.
Technological Advancements
Rapid technological advancements are constantly reshaping the landscape of Im. New tools and platforms emerge frequently, creating both opportunities and complexities. Adapting to these changes and integrating them effectively into existing workflows is crucial for staying competitive and relevant.
The ability to leverage these advancements for improved efficiency and innovation is a significant opportunity.
Data Management and Analysis
Managing and analyzing the vast amounts of data generated by Im is a significant challenge. Effective data management strategies are critical to extracting meaningful insights and making informed decisions. This includes ensuring data security, privacy, and compliance with regulations.
User Experience (UX) Design
Delivering a positive and intuitive user experience is essential for the success of Im. User needs and preferences must be carefully considered throughout the design and development process. This requires ongoing user research and feedback mechanisms to ensure that the product meets its intended goals and aligns with user expectations.
Security and Privacy Concerns
Security and privacy are paramount concerns in Im. Protecting sensitive information and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations is crucial. Robust security measures must be implemented to safeguard user data and prevent unauthorized access. Protecting user privacy is crucial for building trust and maintaining a positive user experience.
Scalability and Sustainability
The ability to scale Im to accommodate increasing user demand and maintain its performance under pressure is essential. Sustainable infrastructure and efficient resource management are critical for long-term success. This includes strategies for adapting to changing user needs and maintaining a high level of performance even as the user base grows.
Collaboration and Integration
Effective collaboration between different teams and departments is essential for the success of Im. Seamless integration with other systems and platforms is crucial for creating a cohesive and user-friendly experience. Facilitating communication and knowledge sharing across teams can be challenging, but it is vital for innovation and efficiency.
Future Directions for NZEB Policies and Incentives

Expanding the Scope of NZEB Policies
A crucial future direction for New Zealand's Net-Zero Energy Building (NZEB) policies lies in broadening their application beyond newly constructed residential and commercial buildings. Current policies predominantly focus on new builds, often neglecting the significant energy consumption and environmental impact of existing structures. This narrow focus misses a vital opportunity to decarbonize the built environment more effectively. To achieve truly widespread reductions in emissions, policies must encompass retrofits and renovations of existing buildings, incentivizing energy efficiency upgrades and the adoption of sustainable technologies.
Furthermore, extending NZEB principles to encompass the entire building lifecycle, from design and construction to operation and eventual demolition, is essential. This holistic approach would promote the use of sustainable materials, encourage the integration of renewable energy sources throughout the building's lifespan, and establish clear guidelines for the responsible disposal and recycling of building materials to minimize environmental harm at the end of a building's life. This comprehensive approach would foster a more sustainable and circular construction industry.
Incentivizing Innovation and Technological Advancement
A key element of future NZEB policies should be to foster innovation and the adoption of cutting-edge technologies. This involves supporting research and development of new, more efficient building materials, advanced insulation techniques, and smart building management systems. These advancements can significantly reduce energy consumption and improve the overall performance of NZEB buildings.
Government funding and tax incentives can play a crucial role in encouraging private sector investment in this area. These incentives should be targeted towards technologies that demonstrate high potential for reducing energy consumption and minimizing environmental impact. Furthermore, the creation of demonstration projects and pilot programs can provide valuable real-world data and insights to inform policy decisions and accelerate the adoption of new technologies.
Collaboration between government agencies, research institutions, and private companies is also critical. This collaborative environment can facilitate the sharing of knowledge, resources, and best practices, ultimately accelerating the development and deployment of innovative NZEB technologies.
Promoting education and training programs for building designers, contractors, and homeowners is equally vital. This will ensure that a skilled workforce is available to implement and maintain NZEB standards, facilitating widespread adoption of these policies. This knowledge transfer can improve the overall efficiency and effectiveness of construction practices.
By prioritizing innovation and technological advancements, New Zealand can position itself at the forefront of sustainable building practices and demonstrate leadership in the global effort to combat climate change.