Climate Risk Mitigation: Real Estate Strategies
Investing in Climate-Forward Real Estate Opportunities

Sustainable Development Goals
Investing in climate-forward real estate is not just about financial returns; it's a crucial step towards achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). By supporting projects that prioritize environmental sustainability, investors contribute to a healthier planet and a more equitable future. This alignment with global sustainability goals can provide long-term value and attract socially conscious investors.
These goals encompass a broad range of issues, from clean energy and poverty reduction to responsible consumption and climate action. Investing in climate-forward real estate directly supports initiatives that address these critical challenges, ensuring a more sustainable future for all.
Energy Efficiency and Renewable Resources
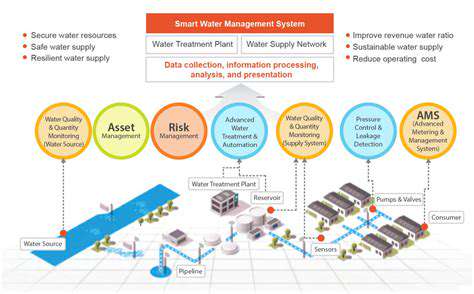
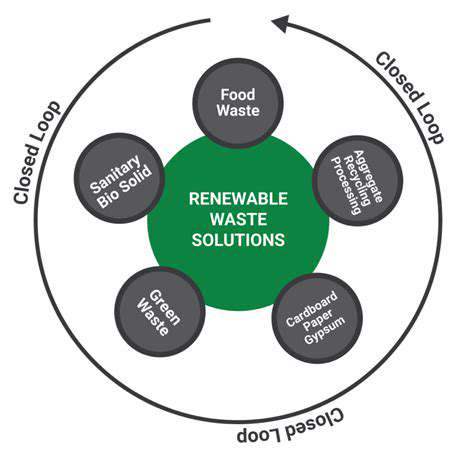
A key aspect of climate-forward real estate is incorporating energy-efficient designs and utilizing renewable resources. This includes optimizing building materials, implementing smart energy management systems, and integrating solar panels or wind turbines. These practices not only reduce the carbon footprint of buildings but also lower operating costs in the long run.
By prioritizing renewable energy sources, investors contribute to the transition towards a low-carbon economy, fostering sustainable development and mitigating climate change.
Resilience to Climate Change Impacts
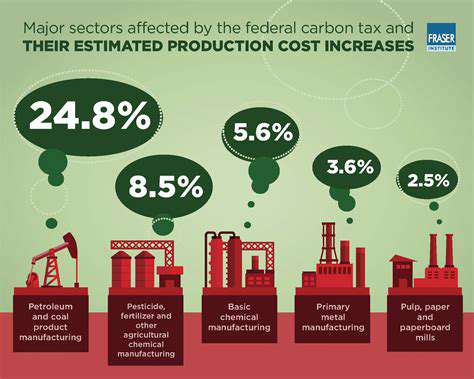
Climate change presents significant challenges to real estate investments, including rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and changing precipitation patterns. Climate-forward real estate strategies must consider these risks and incorporate resilience measures to protect investments and communities. This includes designing buildings to withstand extreme weather conditions and adopting sustainable water management practices.
Green Building Certifications and Standards
Adherence to recognized green building certifications and standards, such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design), is critical for ensuring the environmental performance of climate-forward real estate projects. These certifications verify that buildings meet specific criteria for energy efficiency, water conservation, and material sustainability, providing a reliable benchmark for investors.
These certifications demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and attract environmentally conscious tenants and buyers. Investors gain confidence in the long-term viability and value of these projects.
Community Engagement and Social Equity
Climate-forward real estate extends beyond environmental considerations to encompass social equity and community engagement. This involves creating projects that benefit local communities, promote economic development, and enhance the quality of life for residents. Prioritizing local job creation and affordable housing initiatives alongside sustainability is crucial for community well-being.
Engaging with local stakeholders and ensuring the project aligns with community needs are essential components of a successful climate-forward investment strategy.
Financial Incentives and Government Policies
Many governments offer financial incentives and policies to encourage investment in climate-forward real estate. These incentives can include tax credits, grants, and subsidies for sustainable building practices. Understanding and leveraging these policies is critical for maximizing the financial returns of these investments.
Risk Management and Due Diligence
Investing in climate-forward real estate requires careful risk management and due diligence. Investors need to assess the potential impacts of climate change on the project's long-term viability, considering factors such as extreme weather risks, regulatory changes, and shifting market demands. Thorough analysis of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors is essential for mitigating risks and ensuring responsible investment.
Understanding the potential for disruptions from future climate change scenarios is vital to responsible investment.

Read more about Climate Risk Mitigation: Real Estate Strategies
Hot Recommendations
- Sustainable Real Estate Design Principles
- AI in Real Estate: Streamlining the Buying Process
- Climate Risk Disclosure: A Must for Real Estate
- Climate Risk Analytics: Essential for Real Estate Investment Funds
- Modular Sustainable Construction: Scalability and Speed
- Real Estate and Community Disaster Preparedness
- Smart Buildings and Advanced Building Analytics for Optimal Performance
- Smart Waste Sorting and Recycling in Buildings
- Sustainable Real Estate: A Strategic Advantage
- AI in Real Estate Transaction Processing: Speed and Accuracy